AI for Business: Strategies for Success in Today’s Market
Summary
- AI brings automation and intelligence into core workflows, helping teams offload repetitive tasks, extract insights from large datasets, and make faster, more reliable decisions across key business functions.
- High-impact AI adoption starts by targeting data-heavy, repetitive workflows (such as customer service, finance, marketing, HR, supply chain, sales, and manufacturing) and applying techniques like generative AI, predictive analytics, NLP, and machine learning to drive measurable efficiency and growth.
- Successful AI strategies depend on readiness (data, infrastructure, and culture), clear evaluation and build-vs-buy decisions, a phased roadmap from pilot to scale, strong governance and security, continuous upskilling, and KPIs that tie AI initiatives to operational and business outcomes.
AI is reshaping how organizations build and operate, bringing automation and intelligence into core workflows. Teams use AI to offload repetitive tasks, extract insights from large datasets, and make faster, more reliable decisions. These capabilities are becoming fundamental to how modern businesses scale and compete.
Businesses looking to reap the full benefits of AI need to understand AI capabilities in the context of how they align with the organization’s unique needs. Effective implementation is also essential. A carefully designed, phased strategy helps ensure that AI integration delivers on its full potential.
This blog walks through how to identify high-impact opportunities, select appropriate AI tools and build an adoption roadmap that drives measurable business value
Where AI Can Make an Immediate Impact
AI in business is most effective when applied to clear problems and measurable outcomes. It’s up to each organization to identify areas within the business that would benefit most from AI integration.
Start by mapping core workflows across common business functions – such as finance, HR, customer service, business development and supply chain. Looking at workflows step by step allows you to pinpoint where AI can streamline processes, support business decisions, and provide a deeper understanding of processes and opportunities.
The Business Functions Most Ready for AI Integration
Business functions that rely heavily on data, repetitive tasks and pattern recognition are ideal candidates for AI automation and optimization. These areas typically involve structured processes, predictable workflows and large volumes of information that AI can process faster and more accurately than humans alone. Examples include:
- Customer service: Use AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants to handle routine inquiries, enabling human employees to focus on more complex or relationship-driven interactions. Deep learning and neural networks help these systems analyze unstructured data and user behavior to provide more accurate and personalized responses.
- Finance and accounting: Employ intelligent automation and anomaly detection for high-frequency, rules-based activities such as invoice matching, expense tracking and risk analysis. AI can automate time-consuming tasks, reducing manual effort and improving accuracy.
- Marketing: Analyze customer data to predict buying behavior, generate personalized content and optimize campaigns in real time, empowering teams to deliver more targeted, effective messaging with greater efficiency. Deep learning models and neural networks enable the analysis of unstructured data, such as text and images, and user behavior, allowing for advanced targeting and personalization without much human intervention.
- Human resources: Leverage AI to automate recruitment screening, analyze employee sentiment and forecast turnover risks. By automating time-consuming tasks in the hiring process, HR professionals can focus on more strategic talent acquisition efforts.
- Supply chain and logistics: Utilize AI-driven predictive analytics to optimize inventory levels, anticipate disruptions and improve delivery efficiency.
- Sales: Identify high-potential leads, predict buying behavior, automate CRM updates, generate personalized outreach and leverage real-time insights to help teams close deals more efficiently.
- Manufacturing and transportation: Implement computer vision technologies for automated visual inspection and defect detection, enhancing operational efficiency and product quality.
By pinpointing time-intensive, high-impact areas of the business, organizations can launch AI initiatives that deliver quick wins, demonstrate measurable ROI and lay the groundwork for broader, enterprise-wide transformation.
One example comes from Block, a global technology company committed to making financial services more accessible. Block uses AI-driven automation to simplify onboarding for new business customers on the Square platform by streamlining data imports and setup processes. Sellers can use generative AI tools to automatically produce marketing content, including product descriptions and promotional copy. Businesses can choose from more than 50 creative style prompts and enhance their product images with realistic, AI-generated backgrounds, helping them elevate their online presence, attract new customers and grow.
Key AI Application Types and Their Business Use Cases
Businesses can implement AI applications in many different ways to solve problems, work more efficiently and make better decisions. AI can help organizations analyze large volumes of data to pull actionable insights that support business strategy and drive broader business value.
- Generative AI: Create content, including text, images, audio, video or code. Take on tasks such as brainstorming ideas, writing content ranging from emails to social media posts, generating product images or assisting developers with code completion
- Predictive analytics: Forecast the future using statistical algorithms and historical data. Predictive analytics are used across industries for a variety of functions, including demand forecasting, inventory management, customer churn prediction, supply chain optimization, lead scoring and maintenance scheduling. AI-driven predictive analytics assist businesses in anticipating market trends and optimizing inventory levels, which can enhance decision-making for business leaders by providing data-driven insights for strategic planning.
- Natural language processing (NLP): Based on enabling computers to understand, interpret and generate human language, NLP is key for extracting insights from unstructured data such as emails, reviews and call transcripts. NLP supports market research and business strategy by providing actionable insights from large datasets. Common business applications include sentiment analysis for marketing or HR, customer support chatbots, document summarization and voice assistants.
- Machine learning (ML): ML is the foundation of most AI applications, enabling systems to learn from data to improve performance over time without explicit programming. Businesses apply ML in fraud detection, dynamic pricing, quality control, process optimization and in recommendation engines to suggest products or content. Real-world examples include retailers using ML to optimize inventory and financial institutions leveraging AI for risk assessment.
Readiness Assessment: Does Your Business Have the Prerequisites?
Before you make decisions about AI tools, you need to have the right foundation in place. Businesses ready for AI have identified business pain points or bottlenecks that can be measured and improved. They maintain structured customer data and business records and have strong digital infrastructure and collection practices in place. Culture is key—teams should be encouraged to experiment and refine as they integrate AI.
Business AI and Innovation
How AI Drives Business Model Innovation
AI is rapidly reshaping the business world, empowering organizations to rethink and reinvent their business models. By integrating AI tools such as machine learning, generative AI, and advanced analytics, business leaders can unlock new opportunities for growth and differentiation. AI enables businesses to automate repetitive tasks, allowing teams to focus on higher-value, strategic initiatives that drive innovation.
Integrating AI into business practices not only enhances operational efficiency but also unlocks entirely new products, services, and revenue streams. Business leaders who develop a successful AI strategy position their organizations to gain a competitive edge, adapt to shifting market conditions, and deliver increased value to customers.
Selecting and Adapting AI Tools for Your Business Needs
Once you have a clear understanding of the AI options available and you’re confident that your organization has the infrastructure, data and mindset to embrace them, the next step is to make informed decisions about which AI tools will best serve your company’s unique needs, workflows and long-term strategy. It is crucial to learn how to leverage AI effectively by carefully selecting tools that align with your business goals, developing relevant skills, and managing data strategically.
When evaluating AI tools, consider their features and integration capabilities, as well as important factors, such as security and governance to safely democratize AI across your organization.
Developing a portfolio of AI projects allows organizations to utilize machine intelligence effectively. By diversifying AI initiatives—such as incorporating machine learning, deep learning, and generative models—you can drive innovation, improve efficiency, and manage risks across different business functions.
Evaluation Criteria: Choosing the Right AI Solution
Establishing clear criteria for evaluating AI tools is critical for successful implementation. Criteria should align with your organization’s specific challenges, goals, available resources and priorities. A well-defined evaluation framework helps you compare tools objectively, avoid costly missteps and focus on solutions that deliver measurable value. Common evaluation criteria include:
- Cost considerations: Evaluate the upfront investment, subscription or licensing fees, and any hidden costs associated with implementation, customization or long-term maintenance.
- Measurable ROI: Define clear performance goals, establish success metrics and estimate the expected timeline for achieving a return on the AI investment.
- Integration effort: Determine how well the AI solution integrates with existing systems and understand technical requirements and IT resources needed to support integration.
- Scalability: Ensure the solution can expand with your business, handle increasing data volumes and maintain strong performance as operations grow.
- User-friendliness: Assess how intuitive the platform is to use, how much training teams will need and what level of ongoing support and documentation is available.
- Vendor credibility: Review the provider’s reputation, track record, quality of customer support and frequency of updates to evaluate long-term partnership potential. Pay special attention to the vendor’s security and privacy practices, as robust measures are essential for protecting customer data and maintaining customer trust, especially since data breaches can erode confidence in your company.
- Security and threat response: Evaluate the AI solution’s ability to detect cyber threats and respond to attacks in real-time, safeguarding your business and reinforcing customer trust.
Build vs. Buy: Leveraging Existing AI Tools
Another factor to consider in AI adoption is whether your business would benefit most by purchasing off-the-shelf AI tools and platforms or building custom solutions. Each type offers its own strengths and tradeoffs. Pre-built tools offer speed, simplicity and savings, while custom tools require more investment but provide more flexibility and differentiation.
For most businesses, pre-built solutions offer faster time to value than custom development. Organizations should choose pre-built AI solutions when they need quick, cost-effective results for common tasks such as customer support, marketing automation or forecasting. These tools are easy to deploy, require minimal technical expertise, often come with vendor support and work well for standardized problems.
Building custom AI solutions may be justified when a company wants to leverage proprietary data or has complex workflows that off-the-shelf tools can’t address. For example, companies in sectors such as finance, healthcare or manufacturing may require AI models customized for specific risk factors, patient data or production variables.
Most companies end up doing both—buying foundational capabilities while building the domain-specific intelligence and agentic workflows that differentiate their business.
Building Your AI Adoption Roadmap: From Pilot to Scale
To reach your AI destination, you’ll need an adoption roadmap that provides a step-by-step framework with clear milestones. It’s essential to align this roadmap with your overall business strategy to ensure AI initiatives support organizational goals and drive broader business value.
Phase 1: Running a Strategic AI Pilot
Starting with an AI pilot helps organizations test value, reduce risk and build confidence before scaling. A structured, metrics-focused process ensures clear results and takeaways.
- Select a contained use case: Choose one workflow or department with defined metrics and accessible data to capture clear results.
- Set specific objectives: Define measurable success criteria, such as time savings, accuracy improvements or cost reductions.
- Establish baseline measurements: Document current performance metrics to compare results before and after AI implementation.
- Deploy with limited scope: Implement the AI solution to a small team or subset of customers to simplify monitoring and manage risk.
- Measure and iterate: Track results regularly, gather user feedback and adjust approach to improve outcomes throughout the pilot.
- Document learnings: Capture insights on what worked, what didn’t and why to guide best practices going forward.
Phase 2: Scaling Successful Applications
To progress from an AI pilot to full deployment, start by securing the necessary budget, based on pilot findings and ROI data to demonstrate the value of scaling. Integrate the AI solution into existing systems, such as CRM, ERP or data platforms, to create a seamless flow of information and eliminate data silos as adoption grows. Design processes to maintain performance as usage increases, establishing strong governance policies around data management and model oversight.
People processes are also key. Identify who is responsible for managing systems, resolving issues and making decisions and put a plan in place for AI training.
Measurement and iteration are essential for progress. Create ongoing feedback loops that capture input, track performance trends and continuously improve processes so the AI solution will continue to evolve and deliver value as the organization grows.
Phase 3: Building AI Capabilities Across the Organization
To fully leverage the potential of AI, your teams need to have strong AI literacy. Organizations should provide training and support to build confidence and skills.
A culture of continuous improvement is critical for successful AI adoption. Encourage teams to experiment, measure outcomes and fine-tune processes and approaches. Embedding learning and iteration into daily operations can help businesses evolve from AI users to AI leaders.
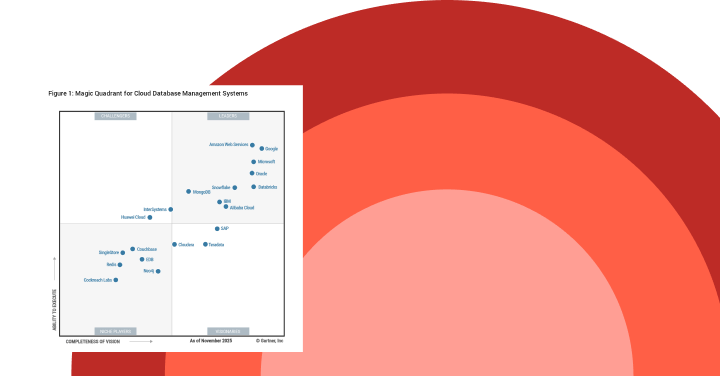
Gartner®: Databricks Cloud Database Leader
Managing the Human Side: Change Management and Team Enablement
AI has the potential to help people move more efficiently, drive greater innovation, and reduce human error. It’s critical for organizations to
Building AI Literacy and Upskilling Your Team
The more understanding and experience people have of AI, the more likely they are to get excited about its potential and actively explore how it can benefit their work. However, employees need opportunities to learn, with a focus on how AI can specifically assist them in their roles. Training should begin with basic AI awareness and progress to more specialized skills relevant to their roles.
Communication Strategies for Stakeholder Buy-In
Different audiences require different messaging strategies to help them understand the value of AI. For example:
Executives: Highlight how AI can contribute to strategic positioning, offer a competitive advantage and provide overall ROI.
Managers: Focus on gains in operational efficiency, reduced workloads, and improved insight.
Employees: Highlight how AI automates tedious tasks and supports skill development, reinforcing that its goal is to make work more effective and efficient.
Customers: Communicate that AI improves service with personalization and faster response times.
Overcoming Common Barriers in AI Adoption
AI adoption planning and implementation also require understanding and preparing for challenges and barriers to implementation. Barriers often include technical limitations and skills gaps. Organizations must pinpoint where AI can meaningfully improve operations.
Many hurdles stem from foundational issues in data, systems, and organizational readiness. Data quality issues, such as incomplete, inconsistent or siloed data, can limit model accuracy and slow down implementation. System compatibility can also be an issue, particularly for organizations that rely on legacy infrastructure.
Adopting cloud-based, unified data platforms designed to support AI can resolve many of these issues.
Skills Gaps and Resource Constraints
Organizations of all sizes often come up against a lack of AI expertise that can hinder AI rollouts. Businesses can turn to:
- Pre-built AI tools that require minimal investment and expertise
- External consultants for initial setup
- Vendor training and support programs
- Targeted, hands-on training to build internal skills
- Pilot programs that grow in-house experience and confidence
Data Privacy, Security and Compliance
Privacy, security and compliance are major areas of concern in AI adoption. Strong data governance, such as access controls and adherence to AI principles, are key to overcoming these roadblocks. Protect sensitive data with data management techniques such as encryption and anonymization that address issues before data is fed into AI models. Businesses must also align systems with regulatory requirements to ensure compliance. Maintain clear documentation and regularly assess systems and performance to head off potential problems.
Measuring AI Success (Supporting section ~300 words)
Measuring AI initiatives is essential to proving business value. Organizations should define metrics that align with strategic goals. To evaluate the impact of AI tools and systems, organizations should establish clear metrics that align with their strategic objectives and business needs.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) for AI projects often include improvements in operational efficiency, cost savings, increased revenue, enhanced customer satisfaction, and reduced error rates. Examples include tracking time saved on repetitive tasks, improvements in prediction accuracy, or the performance of AI-driven fraud detection
It’s essential to establish baseline measurements before implementing AI solutions. Regularly analyzing performance data allows business leaders to identify patterns, optimize processes, and make data-driven decisions about scaling or refining AI applications. Additionally, qualitative feedback from employees and customers can provide valuable insights into how AI is affecting user experience and business operations.
Continuous monitoring and iteration are essential for a successful AI strategy. As AI systems learn and adapt, ongoing measurement ensures that they continue to meet evolving business needs and deliver a competitive advantage. By tying AI outcomes directly to business goals—such as improved supply chain efficiency, faster decision-making, or increased market share—organizations can demonstrate the real-world impact of AI and justify further investment.
Developing Your AI Strategy: Key Takeaways
Businesses of all sizes can successfully integrate AI and capitalize on its capabilities with a step-by-step journey.
- Identify high-impact entry points where AI addresses specific business needs.
- Evaluate tools strategically, considering utility, integration effort and expected ROI.
- Phase implementation from contained pilot to scaled deployment.
- Manage change through communication, training and stakeholder engagement.
- Address barriers practically by setting realistic expectations and implementing practical workarounds.
AI adoption is a big undertaking. Developing the skills and processes for AI adoption now allows you to build your AI expertise, positioning your organization to maximize AI value and stand ready for new opportunities.
Never miss a Databricks post
What's next?
Data + AI Foundations
February 3, 2026/9 min read