BP’s Geospatial AI Engine: Transforming Safety and Operations with Databricks
How BP Built a Real-Time Geospatial Platform on Databricks to Improve Safety and Reduce Risk

Summary
- How BP built a real-time geospatial platform using Databricks, Event Hub, and Azure Data Lake.
- How AI and machine learning power collision detection, alerts, and advanced spatial analysis.
- How BP’s One Map platform improves safety, planning, and operational efficiency across global operations.
The integration of DATABRICKS capabilities with geospatial technology marks a significant advancement in the field of geo-computing. By effectively addressing the challenges associated with real-time geospatial data analytics and leveraging state-of-the-art technologies, bp has set a new industry standard for enterprise architecture in the energy sector. Led by Steven Bjerring, Senior Manager of bp’s Geospatial Oil and Gas Technology team, this initiative has produced an architectural framework that uses advanced geo-computing to improve safety, efficiency, and innovation via geospatial data processing.
Challenge: Real-Time Geospatial Data Analytics
Faced with the challenge of real-time monitoring and analysis of extensive geospatial datasets, including both vector and raster data from sources such as vessels, aircraft, radar systems, robotics, sensors, and IoT devices; efficient data ingestion, aggregation, and processing were imperative to support critical functions like Collision Detection, Buffer Analysis, and Vessel Arrival Notifications.
To address these complex requirements, bp implemented scalable cloud-based architectures and advanced machine learning algorithms to automate anomaly detection and event prediction across multiple data streams. The initiative prioritized the optimization of data pipelines to achieve low-latency processing, thereby facilitating timely and informed decision-making.
Robust data standardization and industry standard APIs enabled interoperability, reduced silos, and supported safety, efficiency, planning, and compliance. BP quickly processed terabytes of raster data for timely analysis.
Solution: Integrating DATABRICKS with Geospatial Technology
To address these challenges, bp utilized DATABRICKS features and incorporated them into its geospatial platform, One Map, resulting in a comprehensive and scalable system. Geospatial data is streamed via the Event Hub infrastructure and stored in the Azure Data Lake environment. This process enables real-time queries and allows for the concurrent collection of up-to-date geospatial transactional data.
By leveraging DATABRICKS features, bp was able to integrate advanced analytics and data processing capabilities, which facilitated faster analysis and improved decision-making across various departments. The Event Hub acts as a robust data ingestion layer, efficiently streaming large volumes of geospatial data from multiple sources, including IoT devices and remote sensors, into the platform. Once ingested, the Azure Data Lake provides a secure and flexible storage solution, allowing for structured and unstructured data to be accessed and processed as needed.
Real-time queries empower users to interact dynamically with ever-changing geospatial datasets, supporting applications such as asset tracking, resource management, and spatial analysis. Simultaneously, the system's ability to collect and update transactional data ensures that all stakeholders have access to the most current information, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and enabling timely responses to emerging trends or incidents within bp’s global operations.
Here are a couple of key screen shares to illustrate:
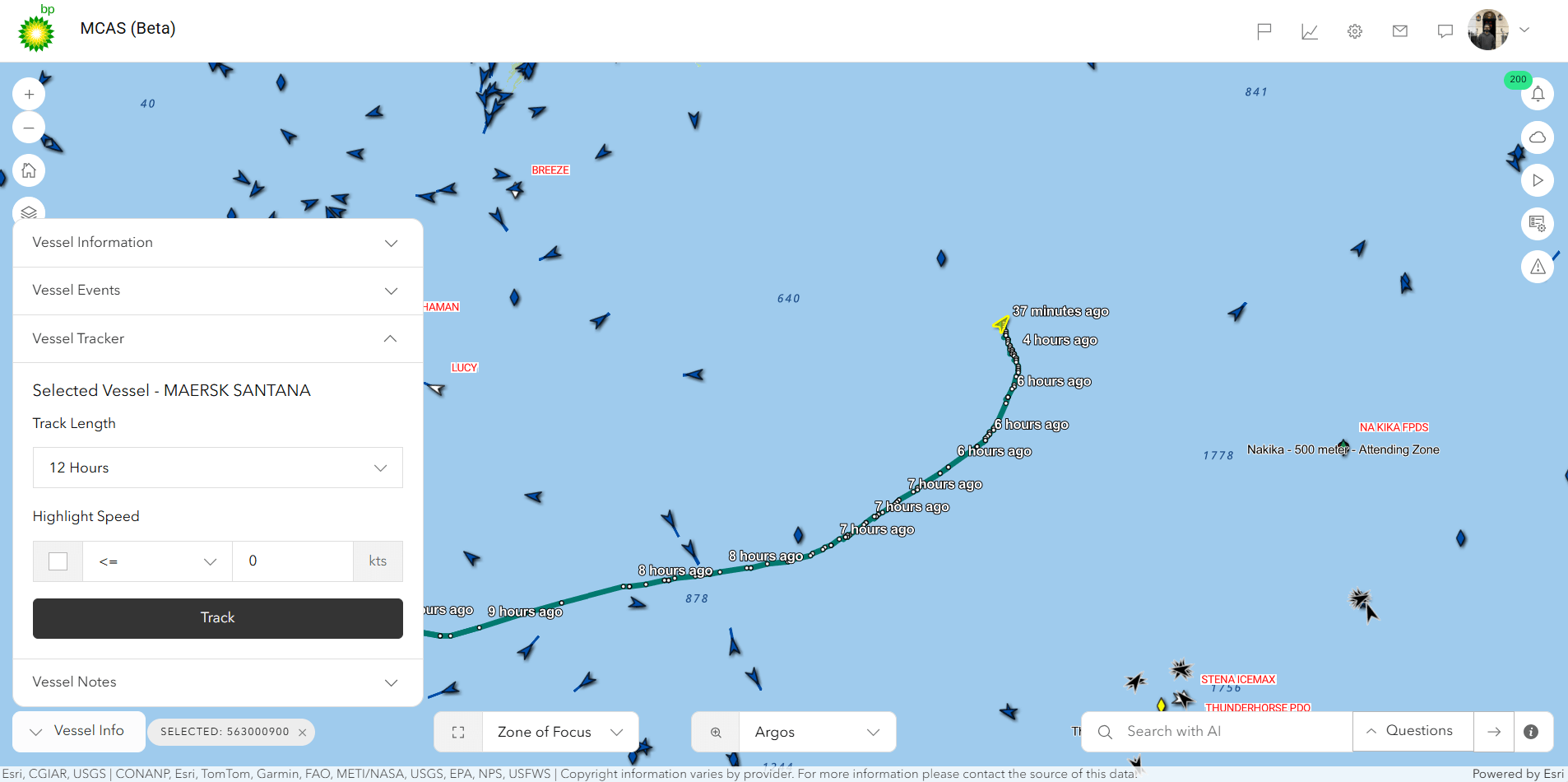
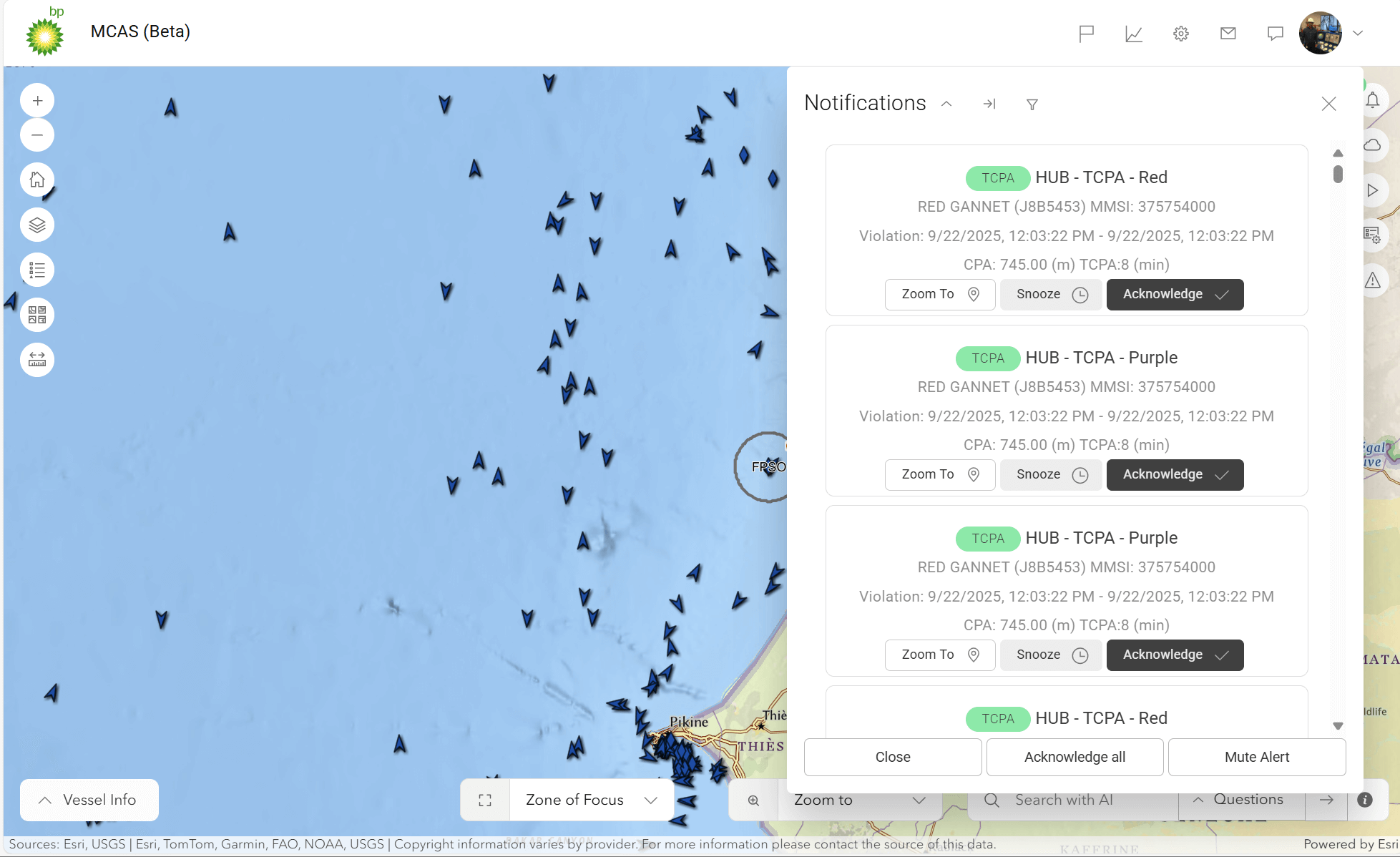
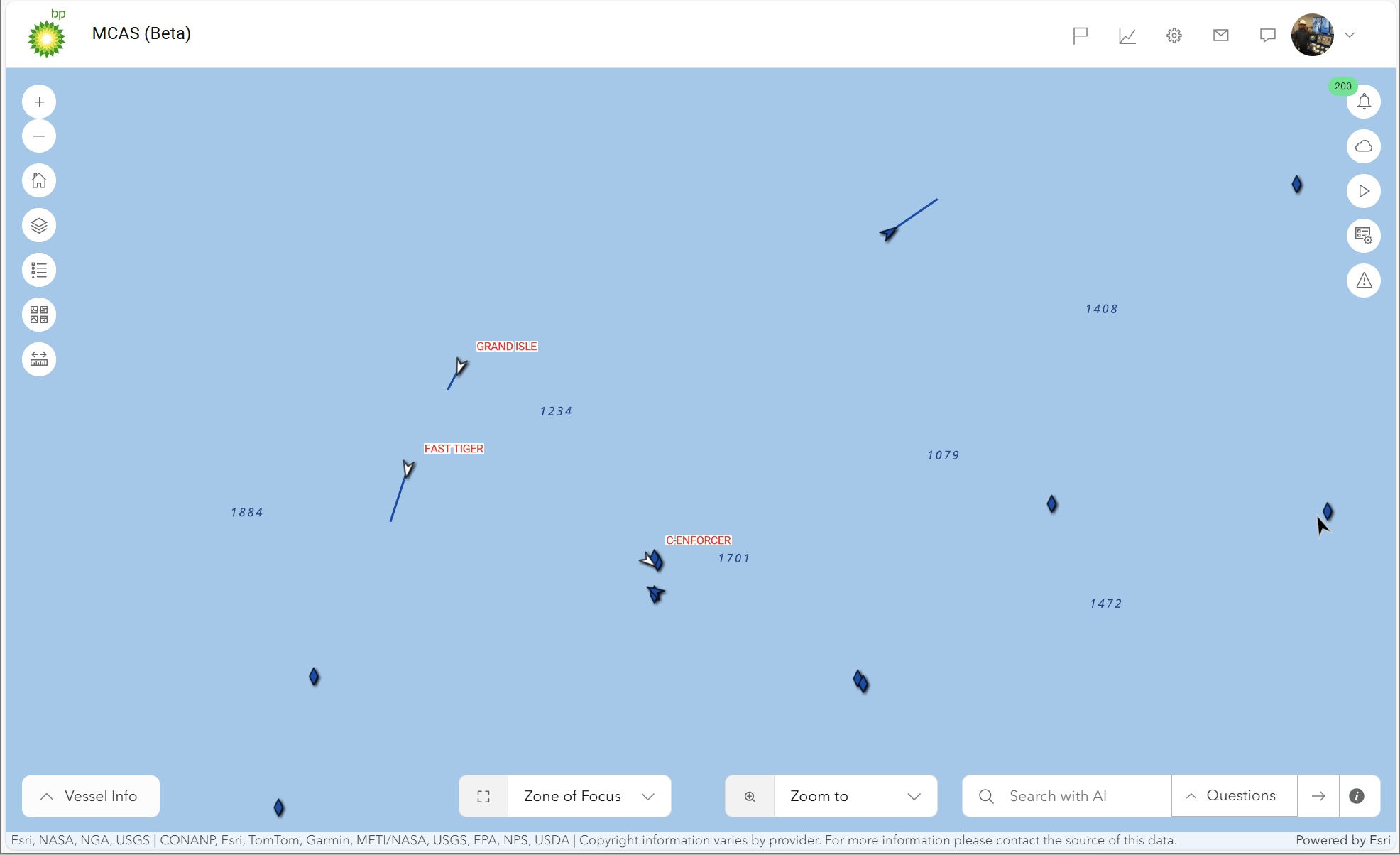
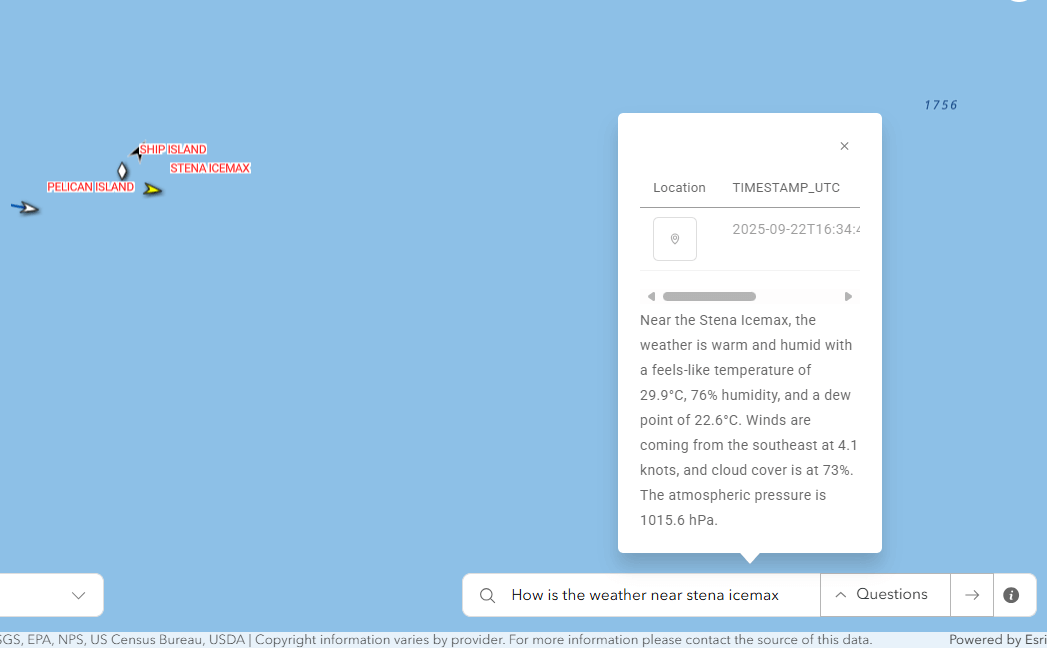
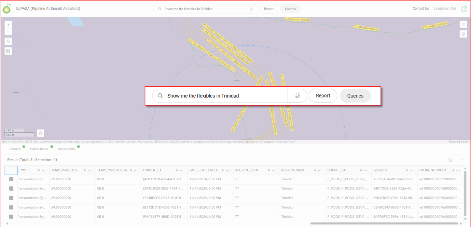
One Map AI Engine: The One Map AI Engine serves as the core support for these applications, utilizing multiple workflows to minimize Notification and Alert noise, aggregate data, and integrate APIs such as Weather and Radar to deliver a comprehensive overview. These demonstrations effectively illustrate the measurable advantages gained from bp’s strategic technology integration, where advanced innovation meets practical implementation to optimize geospatial intelligence utilization. The strength of this ecosystem is derived not only from its forward-thinking use cases but also from the resilient architecture and carefully chosen technologies that drive the platform.
AI underpinnings of bp’s solution requires an examination of the foundational technologies and architectural principles that underpin this transformative integration.
Data intelligence reshapes industries
Key Technologies and Architecture
The solution leverages several key technologies:
- Databricks: A unified analytics platform built on Apache Spark, Databricks processes, analyses, and visualizes large datasets. It provides a collaborative environment for data engineers, scientists, and analysts, offering interactive notebooks, efficient cluster management, and machine learning capabilities.
- Delta Live Table: Continuously updated with real-time streaming data, Delta Live Tables maintain transactional integrity and optimize query performance, allowing seamless integration of real-time data streams into a structured format.
- Kafka Connector (Azure Event Hub): This connector links Apache Kafka with other data systems, efficiently moving data between Kafka and external sources, enhancing scalability and fault tolerance.
- SQL Data Warehouse: Designed for the analysis of substantial data volumes, SQL data warehouses employ columnar storage and parallel processing to facilitate rapid querying and the extraction of insights.
- Databricks Genie: The implementation of GenAI allows our users to engage with this advanced technology through natural language, thereby improving operational efficiency. We have designed this to help us query our datasets spatially while returning natural language response along with spatial attributes, which then is utilized in the widget to integrate with the application itself to visualize the results.
- Raster Data Processing: Interaction with various py modules like ArcGIS Py, GDAL, Multispectral Image Processing etc. To name a few.
The Significance: Advancing Geospatial Data Processing
Steven Bjerring, Senior Manager envisioned an innovative and forward-thinking approach to geospatial data processing, facilitating rapid generation of data, statistics, and analytics to address critical challenges while maintaining low costs, minimizing downtime, and ensuring usability and scalability. With bp’s established expertise as outlined by Emeka Emembolu (EVP Technology) in big data analytics and its strategic integration of geospatial and platform teams, the organization is well positioned to drive advancements in this field.
This visionary method holds promise for transforming how organizations respond to dynamic environments and complex problems. By harnessing advanced analytics and seamless collaboration between specialized teams, bp can unlock deeper insights into spatial patterns and trends, support more informed decision-making, and optimize operational performance. The scalable nature of this solution also paves the way for expansion into new domains, such as environmental monitoring, infrastructure planning, and resource management, ultimately positioning bp at the forefront of digital innovation within the energy sector.