AI Transformation: A Complete Strategy Guide for 2025
Learn why 80% of organizations fail to scale AI beyond pilots and discover the proven framework for transforming process, people, and platform to achieve 3.7x ROI

The release of ChatGPT in November 2022 fundamentally changed expectations about artificial intelligence. According to McKinsey's latest survey, nearly nine out of ten organizations now regularly use AI—yet less than 20% have successfully scaled beyond pilot projects. This gap reveals a crucial truth: successful AI transformation isn't about deploying technology—it's about redesigning how your business operates.
Organizations achieving measurable impact understand that AI transformation requires a comprehensive strategy spanning process, people, and platform. This guide provides a proven framework for accelerating from pilots to production at scale.
Understanding AI Transformation in the Modern Enterprise
AI transformation is the strategic integration of AI across operations, products, and services to drive innovation and competitive advantage. Unlike digital transformation initiatives focused on modernizing infrastructure, this means evolving from automating routine tasks to deploying AI agents that handle complex workflows with unprecedented autonomy.
The modern enterprise must treat AI as transformative, not just another tool. Organizations leveraging AI successfully don't simply add capabilities to existing processes—they rethink operating models entirely. IDC research shows that for every dollar invested in generative AI, organizations realize an average ROI of 3.7x, with top leaders achieving returns of 10.3x.
The Current State of AI Adoption
Gen AI usage jumped from 55% in 2023 to 75% in 2024. Survey respondents across industries report using AI in at least one business function, with marketing, sales, and customer service leading adoption rates.
Despite widespread experimentation, most organizations struggle with scaling AI beyond pilots. The challenge isn't technological—it's organizational. Companies treating gen AI as technology deployment rather than business transformation leave pilot projects stranded, unable to deliver measurable impact that leadership teams demand.
AI high performers—organizations attributing 5% or more EBIT impact to AI use—share common traits: bold ambitions, redesigned workflows, faster scaling, and significantly higher investment in AI capabilities compared to their peers.
Why Most AI Transformations Fail
Many organizations underestimate the scope required to put data and AI to work effectively. The most common failure is treating transformation as a one-time effort rather than continuous evolution.
Critical factors derail AI initiatives: insufficient alignment between business strategy and investments means projects lack clear ties to business outcomes. Weak data governance creates shaky foundations—bad data in means bad data out. Cultural resistance and inadequate change management prevent adoption. Finally, spreading AI tools too thin across hundreds of use cases prevents any from reaching scale needed for meaningful impact.
The Process Framework: Building Your AI Strategy
Establish Your North Star Strategy
The critical first step is developing a comprehensive plan for driving measurable business results against corporate priorities. This strategy serves as principles every member can reference when making decisions. Define your North Star—for many, it's democratizing access to data and leveraging AI to drive innovation.
Your strategy must align with business goals, not technology trends. What specific business outcomes do you need? How will AI help? What does success look like—revenue growth, cost reductions, improved customer satisfaction?
Organizations achieving real progress set bold ambitions early. They aim to transform entire business functions, create new revenue streams, or fundamentally change customer experience. This level of ambition separates companies stuck in pilot mode from those scaling AI enterprise-wide.
Start with Governance as Foundation
Data governance is foundational to your strategy. Effective governance answers: Do you have correct data for use cases? Is data high quality and timely? Do the right people have appropriate access? How do people find what they need?
Strong governance becomes critical as you integrate AI technologies into operations. You need policies managing unique risks: algorithmic bias, privacy concerns, and explaining AI-driven decisions. Without governance, you risk deploying systems making decisions based on flawed or biased data.
Modern governance emphasizes enablement, not restriction. The goal is creating frameworks where data scientists, data engineers, and analysts access the right data quickly while automatic controls ensure regulatory compliance, security, and quality. This balance between control and autonomy enables moving fast without breaking things.
Leveraging Generative AI Strategically
The explosion of gen AI creates opportunities and risks of chasing the cool factor. Successful organizations focus on use cases driving genuine business value rather than deploying everywhere.
Start by identifying where AI initiatives deliver measurable outcomes. Common starting points include automation of repetitive tasks, enhancement of business processes through intelligent assistance, and augmentation of decision-making with data analysis.
The crawl-walk-run approach proves effective. Begin with lower-risk opportunities offering near-term productivity gains. As you build capabilities, expand to complex use cases transforming core business functions. Many companies start with AI-powered content or customer service before moving to sophisticated applications like predictive maintenance.
AI agents and agentic AI represent the next frontier—systems handling complex workflows autonomously. However, successfully deploying agentic AI requires mature infrastructure, refined models, and redesigned business processes accounting for human-machine collaboration.
Remember: data is 100% the foundation of success. The most sophisticated models can't overcome poor data practices.
The Build vs. Buy Decision
A key component involves deciding which ecosystem components to build versus purchase. The primary factor should be whether a solution offers true competitive advantage. Does building this make it harder for competitors? If no, focus resources on activities providing differentiation.
If you decide something provides advantage worth building, consider time-to-market implications. Software projects typically take longer, require specialized talent, and cost more than planned. Most companies succeed by buying platforms providing strong foundations, then building applications delivering unique market value.
Define Success Metrics
Establishing clear metrics is essential for tracking progress and demonstrating value. Track adoption metrics: percentage of employees using AI tools, number of business functions deploying solutions, data volume flowing through systems.
Measure business outcomes directly: revenue increases from AI-powered products, cost reductions from automated workflows, customer satisfaction improvements, time saved on processes. Organizations seeing greatest impact track EBIT contributions specifically attributable to initiatives.
The People Dimension: Enabling AI Organization-Wide
Understanding Your Organization's Needs
Successful transformation starts with understanding people in your organization—their roles, goals, and how they want interacting with technologies. Data scientists need raw data and advanced models. Data engineers need infrastructure for building pipelines. Business analysts want self-service insights without coding. Senior leaders need dashboards surfacing recommendations.
Meeting users where they are encourages adoption and collaboration. Provide multiple interfaces: APIs for developers, no-code platforms for business users, notebook environments for scientists. The goal is democratizing capabilities across your organization.
Balance Centralized Control with Distributed Autonomy
Determining what to control centrally versus allowing autonomy is challenging. Successful organizations establish clear non-negotiables while giving teams freedom to innovate within boundaries.
Centralized control focuses on foundations: architectural principles, data governance policies, security standards, regulatory compliance requirements. These create guardrails ensuring initiatives meet minimum standards. Within these, give teams autonomy through self-service access to data, building models, and deploying solutions without waiting for approvals.
This approach enables enterprise-wide collaboration essential for maximizing value. When marketing teams easily access customer insights from sales systems, or product teams leverage usage data from customer success tools, you break down silos limiting business value.
Empowering Your Workforce
Training and change management determine whether people embrace AI or resist it. Getting change management right is more complex than implementing technology.
Successful organizations have internal change agents leading initiatives from within. They create communities of practice sharing best practices, run competitions gamifying adoption, and celebrate early wins demonstrating value.
Training should span multiple levels. Basic literacy helps everyone understand what AI can and can't do. Functional training teaches using tools relevant to roles. Advanced training develops capabilities in technical staff building and maintaining systems.
Remember: people want to be successful. When you provide clear paths—training, support, recognition—most embrace transformation enthusiastically, seeing AI as amplifying capabilities rather than replacing them.
The Platform Architecture: Technology Foundations
Simplify Your Technology Stack
The move to cloud computing unlocked flexibility but introduced complexity. When evaluating technologies for your stack, remember less is often more. Every additional tool creates integration challenges, increases learning curves, and adds maintenance overhead.
The principle of consolidation applies especially to data estates. Multiple data silos make transformation exponentially harder. Evaluate whether each platform provides unique value or if consolidation could deliver same capabilities with less complexity.
Data Infrastructure Requirements
Clean, accessible, connected data is essential for implementation. Your infrastructure must support real-time data pipelines integrating across enterprise systems, data quality management maintaining accuracy, security protocols protecting sensitive information while enabling access, and scalable storage growing with increasing needs.
Infrastructure also needs supporting the full lifecycle: data ingestion, transformation, feature engineering, model training, deployment, and monitoring performance over time.
Future-Proof with Open Standards
Open standards and open source solutions provide crucial advantages for long-term success. Storing data in open formats ensures you can access it using any tool, not just current vendor products. This portability means changing course without expensive migrations.
Open source frameworks accelerate innovation. Technologies like PyTorch and TensorFlow have massive communities contributing improvements. When you build on these foundations, you benefit from collective intelligence.
The Lakehouse Architecture Advantage
Traditional approaches forced organizations choosing between data warehouses optimized for analytics and data lakes optimized for machine learning. The lakehouse architecture solves this by providing a unified system for all enterprise data and all workloads.
A lakehouse combines the best aspects: flexibility and cost-effectiveness of storing all data in open formats with performance and reliability of warehouses. This proves essential because models need access to comprehensive data.
With a lakehouse, your scientists train machine learning on the same data your analysts query for reports. Agents access transactional, historical, and unstructured data without moving it between systems. This eliminates synchronization challenges and governance complexity plaguing traditional architectures.
Migration Strategy: Lift, Modernize, Shift
When migrating to cloud infrastructure enabling transformation, organizations consider two approaches. Lift-and-shift moves existing systems with minimal changes, then modernizes later. Lift-modernize-shift redesigns systems for cloud-native architectures before migration.
In practice, lift-and-shift disappoints. What seems faster proves more expensive, takes longer, and delivers less value. The lift-modernize-shift approach succeeds despite requiring more upfront work. By redesigning your architecture for cloud and AI during migration, you avoid double-transition penalties.
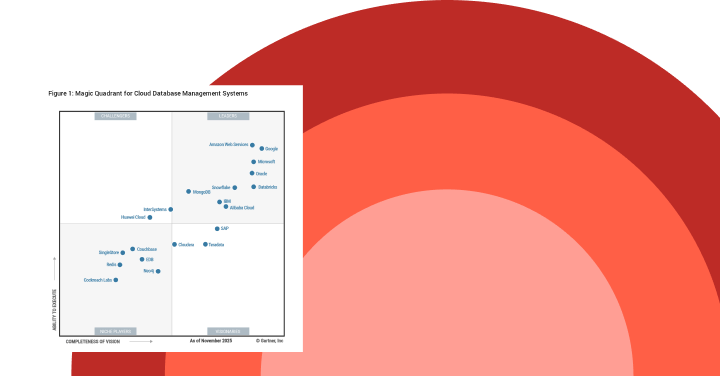
Gartner®: Databricks Cloud Database Leader
Putting It All Together: The Transformation Roadmap
Phase 1: Foundation Building
Your journey begins establishing foundations enabling everything else. This phase typically takes 3-6 months but proves essential for long-term success.
Start assessing current infrastructure: Where is data stored? What's the quality? Who has access? This audit reveals gaps needing addressing before scaling initiatives.
Establish strong governance frameworks early. Define policies for classification, access control, quality standards, and retention. Implement technical infrastructure enforcing policies automatically. Build executive sponsorship through education and pilot projects.
Phase 2: Scaling AI Initiatives
With foundations in place, scaling focuses on expanding successful pilots to production systems delivering measurable business value.
Moving from pilots to production requires redesigning workflows to integrate AI seamlessly. Instead of asking people using tools separately, embed capabilities into systems and processes they already use.
Expand across business functions systematically. Prioritize based on business impact and feasibility. Functions with clean data, clear metrics, and leadership buy-in make better early targets.
Phase 3: Enterprise-Wide Transformation
The final phase involves AI becoming deeply embedded in how your organization operates. At this stage, it's not a special project—it's part of your operating model.
Agents handling complex workflows represent a key milestone. Instead of assisting humans, systems autonomously execute multi-step processes, only escalating when encountering ambiguity.
Operating models redesigned for AI reflect fundamental changes in how work gets done. Teams become smaller as AI handles routine tasks. Decision cycles accelerate as AI provides real-time insights. New roles emerge focused on managing systems.
Continuous innovation characterizes mature adoption. Rather than completing transformation and being done, you maintain permanent capabilities for identifying new use cases, experimenting with emerging technologies, and evolving systems as needs change.
Industry Applications and Common Pitfalls
While principles apply broadly, successful implementation looks different across industries. In healthcare and life sciences, transformation drives drug discovery through molecular analysis. Financial services leverages AI for fraud detection and risk assessment. Manufacturing applies AI to predictive maintenance and quality control. Retail uses AI extensively for customer experience enhancements.
The biggest mistake is treating transformation as a one-time effort rather than continuous evolution. Organizations complete projects, declare victory, and return to business as usual. Then they wonder why capabilities stagnate while competitors pull ahead.
Spreading tools too thin prevents any from reaching scale needed for meaningful impact. Ignoring regulatory compliance creates enormous risk. Underestimating change management leads to technically successful systems nobody uses.
Measuring and Sustaining Success
Measuring transformation requires metrics spanning tactical operations through strategic business impact. Business outcomes provide the ultimate measure. Revenue growth driven by AI-powered products demonstrates top-line impact. Cost reductions from automated workflows prove bottom-line benefits.
Operational efficiency metrics reveal whether AI is streamlining operations. Time saved on repetitive tasks, reduced error rates, faster cycle times—these indicate AI delivering productivity gains.
Customer satisfaction improvements warrant close monitoring, particularly for customer-facing applications. Track Net Promoter Score, effort scores, and satisfaction ratings for AI-assisted versus human-only interactions.
Building for the long term requires lifecycle management, continuous model improvement, adapting to new technologies, and maintaining competitive advantage through continuous innovation.
The Transformation Imperative
AI transformation represents a fundamental shift in how businesses operate and compete. Organizations that started their journey early have demonstrated enormous potential: productivity gains of 40% or more for key workflows, revenue increases from AI-powered innovations, and cost reductions fundamentally changing competitive position.
But meaningful transformation takes time, sustained investment, and unwavering commitment from leadership. It's not about deploying a few tools and declaring victory. It's about systematically building process, people, and platform capabilities enabling AI to transform your business at every level.
Success requires all three pillars working together. The best platform won't deliver value without right processes for governance, prioritization, and measurement. The most sophisticated strategy fails without people having skills, motivation, and support to implement it.
Start your journey today. Begin with foundations: establish governance, build executive sponsorship, and run focused pilots proving value. Scale systematically: prioritize high-impact opportunities, redesign workflows, and invest in change management. Aim for enterprise-wide transformation: embed AI in your operating model, maintain continuous innovation capabilities, and treat AI as central to competitive strategy.
The modern enterprise mastering transformation doesn't just automate routine tasks or marginally improve existing processes. It fundamentally reimagines what's possible, creates value in novel ways, and competes on dimensions unavailable to rivals without mature capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is AI transformation?
AI transformation is the strategic initiative whereby an organization adopts and integrates artificial intelligence across its operations, products, and services to drive innovation, efficiency, and growth. Unlike traditional technology deployments, it involves fundamentally redesigning business processes, operating models, and decision-making approaches to leverage AI capabilities. Successful transformation requires changes across three dimensions: process (governance, strategy, metrics), people (skills, culture, change management), and platform (data infrastructure, tools, technical architecture). The goal is becoming an AI-driven organization where intelligent systems augment human capabilities throughout the enterprise.
What are the 4 types of AI technology?
The four major categories transforming enterprises today include: (1) Machine Learning systems that learn patterns from historical data to make predictions and classifications; (2) Generative AI including large language models that create new content—text, images, code generation, or other media—based on training data; (3) Agentic AI systems that autonomously execute complex multi-step workflows with reasoning capabilities, handling tasks from start to finish with minimal human intervention; and (4) Traditional AI encompassing rule-based systems, robotic process automation, and deterministic algorithms that follow explicit programmed logic. Modern transformations typically leverage a mix of these technologies, choosing the appropriate type based on specific use cases, available data, and required capabilities.
What is the 30% rule for AI?
The 30% rule in AI contexts most commonly relates to the threshold for meaningful adoption and measurable impact. Research suggests that organizations seeing less than 30% adoption of tools by target users typically fail to achieve significant value, as network effects and workflow integration require critical mass to deliver returns. Another interpretation relates to findings that approximately 30% of tasks in most knowledge worker roles can be augmented or automated by current technologies—high enough to deliver substantial productivity gains through streamlining operations, but not so high that wholesale job displacement occurs. The principle emphasizes that successful transformation requires reaching sufficient scale and impact rather than settling for marginal improvements that don't justify the significant investment and change management costs involved.
Never miss a Databricks post
What's next?

Data Science and ML
June 12, 2024/8 min read
Mosaic AI: Build and Deploy Production-quality AI Agent Systems
AI
January 7, 2025/6 min read