Reverse ETL with Lakebase: Activate your lakehouse data for operational analytics
Serve data from the lakehouse to applications reliably and at scale, without custom pipelines.
Summary
- Reverse ETL is the process of making curated lakehouse data actionable, making it available to apps, dashboards, and CRM systems.
- Lakebase eliminates the need for custom pipelines, syncing gold-layer data directly into a fully-managed Postgres database.
- Lakebase supports low-latency use cases like ML-powered support dashboards, segmentation engines, and personalized user experiences, all with the power and extensibility of Postgres.
Introduction: Analytics and operations are converging
Applications today can’t rely on raw events alone. They need curated, contextual, and actionable data from the lakehouse to power personalization, automation, and intelligent user experiences.
Delivering that data reliably with low latency has been a challenge, often requiring complex pipelines and custom infrastructure.
Lakebase, recently announced by Databricks, addresses this problem. It pairs a high-performance Postgres database with native lakehouse integration, making reverse ETL simple and reliable.
What is reverse ETL?
Reverse ETL syncs high-quality data from a lakehouse into the operational systems that power applications. This ensures that trusted datasets and AI-driven insights flow directly into applications that power personalization, recommendations, fraud detection, and real-time decisioning.
Without Reverse ETL, insights remain in the lakehouse and don’t reach the applications that need them. The lakehouse is where data gets cleaned, enriched, and turned into analytics, but it isn’t built for low-latency app interactions or transactional workloads. That’s where Lakebase comes in, delivering trusted lakehouse data directly into the tools where it drives action, without custom pipelines.
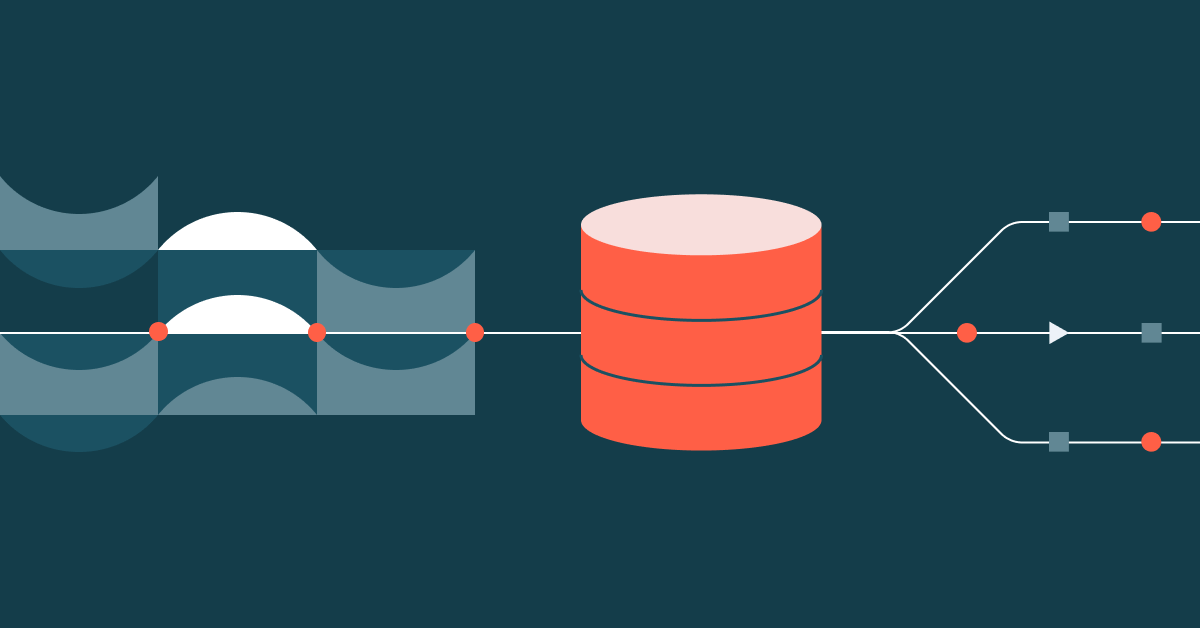
In practice, reverse ETL typically involves four key components, all integrated into Lakebase:
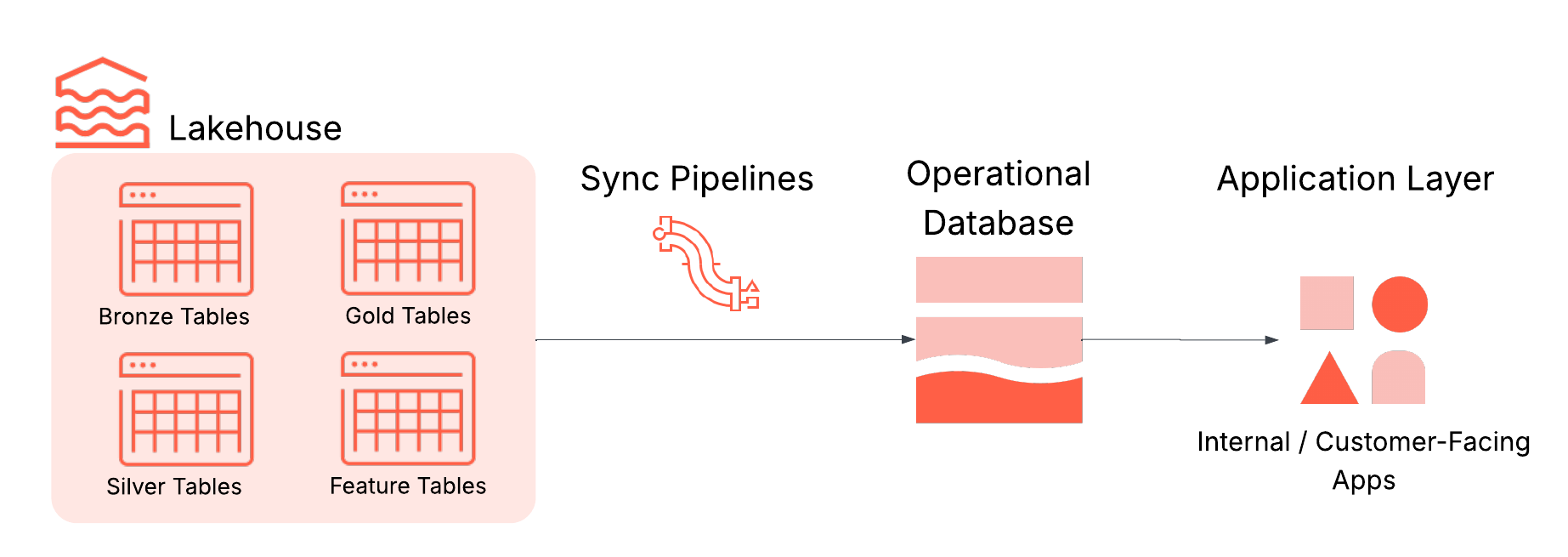
- Lakehouse: Stores curated, high-quality data used to drive decisions, such as business-level aggregate tables (aka “gold tables”), engineered features, and ML inference outputs.
- Syncing pipelines: Move relevant data into operational stores with scheduling, freshness guarantees, and monitoring.
- Operational database: Optimized for high concurrency, low latency, and ACID transactions.
- Applications: The final destination where insights become action, whether in customer-facing applications, internal tools, APIs, or dashboards.
Challenges of reverse ETL today
Reverse ETL looks simple but in practice, most teams run into the same challenges:
- Brittle, custom-built ETL pipelines: These pipelines often require streaming infrastructure, schema management, error handling, and orchestration. They’re brittle and resource-intensive to maintain.
- Multiple, disconnected systems: Separate stacks for analytics and operations mean more infrastructure to manage, more authentication layers, and more chances for format mismatches.
- Inconsistent governance models: Analytical and operational systems usually live in different policy domains, making it hard to apply consistent quality controls and audit policies.
These challenges create friction for both developers and the business, slowing down efforts to reliably activate data and deliver intelligent, real-time applications.
Lakebase: Integrated by default for easy reverse ETL
Lakebase removes these barriers and transforms reverse ETL into a fully managed, integrated workflow. It combines a high-performance Postgres engine, deep lakehouse integration, and built-in data synchronization so that fresh insights flow into applications without extra infrastructure.
These capabilities of Lakebase are especially valuable for Reverse ETL:
- Deep lakehouse integration: Sync data from lakehouse tables to Lakebase on a snapshot, scheduled, or continuous basis, without building or managing external ETL jobs. This replaces the complexity of custom pipelines, retries, and monitoring with a native, managed experience.
- Fully-managed Postgres: Built on open source Postgres, Lakebase supports ACID transactions, indexes, joins, and extensions such as PostGIS and pgvector. You can connect with existing drivers and tools like pgAdmin or JDBC, avoiding the need to learn new database technologies or maintain separate OLTP infrastructure.
- Scalable, resilient architecture: Lakebase separates compute and storage for independent scaling, delivering sub-10 ms query latency and thousands of QPS. Enterprise-grade features include multi-AZ high availability, point-in-time recovery, and encrypted storage, removing the scaling and resiliency challenges of self-managed databases.
- Integrated security and governance: Register Lakebase with Unity Catalog to bring operational data into your centralized governance framework, covering audit trails and permissions at the catalog level. Access via Postgres protocol still uses native Postgres roles and permissions, ensuring authentic transactional security while fitting into your broader Databricks governance model.
- Cloud-agnostic architecture: Deploy Lakebase alongside your lakehouse in your preferred cloud environment without re-architecting your workflows.
With these capabilities in the Databricks Data Intelligence Platform, Lakebase replaces the fragmented reverse ETL setup that relies on custom pipelines, standalone OLTP systems, and separate governance. It delivers an integrated, high-performance, and secure service, ensuring that analytical insights flow into applications more quickly, with less operational effort, and with governance preserved.
Sample Use Case: Building an Intelligent Support Portal with Lakebase
As a practical example, let’s walk through how to build an intelligent support portal powered by Lakebase. This interactive portal helps support teams triage incoming incidents using ML-driven insights from the lakehouse, such as predicted escalation risk and recommended actions, while allowing users to assign ownership, track status, and leave comments on each ticket.
Lakebase makes this possible by syncing predictions into Postgres while also storing updates from the app. The result is a support portal that combines analytics with live operations. The same approach applies to many other use cases including personalization engines and ML-driven dashboards.
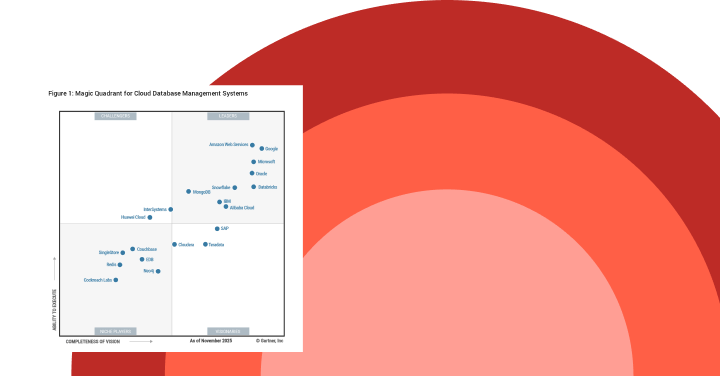
Gartner®: Databricks Cloud Database Leader
Step 1: Sync Predictions from the Lakehouse to Lakebase
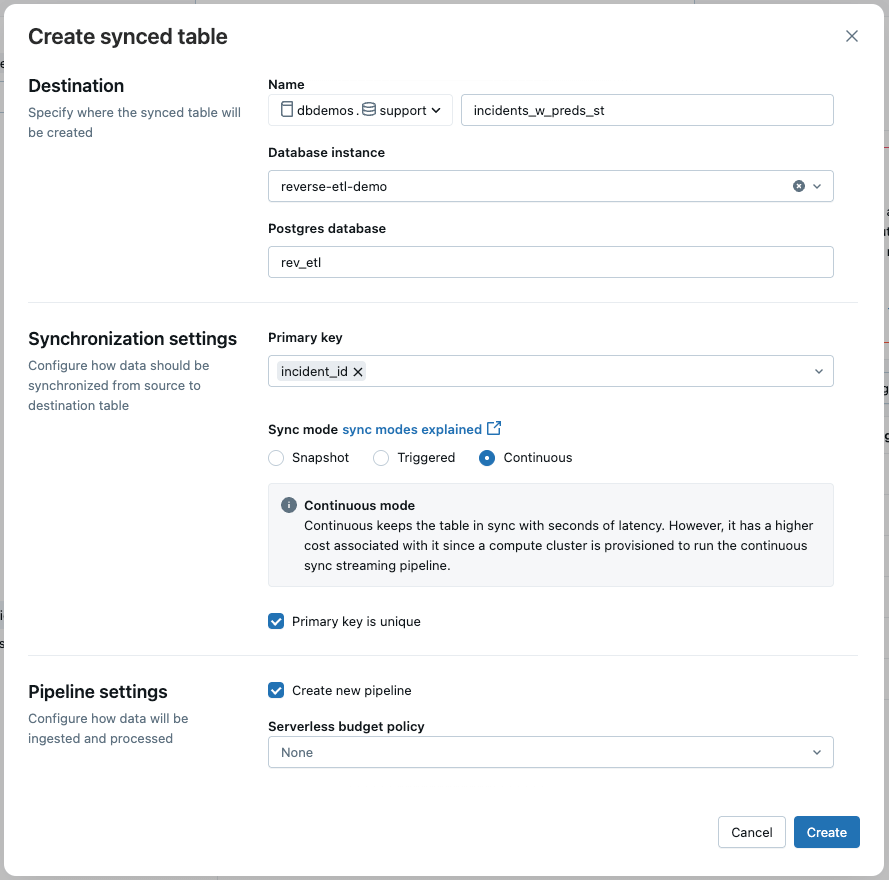
The incident data, enriched with ML predictions, lives in a Delta table and is updated in near real-time via a streaming pipeline. To power the support app, we use Lakebase reverse ETL to continuously sync this Delta table to a Postgres table.
In the UI, we select:
- Sync Mode: Continuous for low-latency updates
- Primary Key: incident_id
This ensures the app reflects the latest data with minimal delay.
Note: You can also create the sync pipeline programmatically using the Databricks SDK.
Step 2: Create a State Table for User Inputs
The support app also needs a table to store user-entered data like ownership, status, and comments. Since this data is written from the app, it should go into a separate table in Lakebase (rather than the synced table).
Here’s the schema:
This design ensures that reverse ETL stays unidirectional (Lakehouse → Lakebase), while still allowing interactive updates via the app.
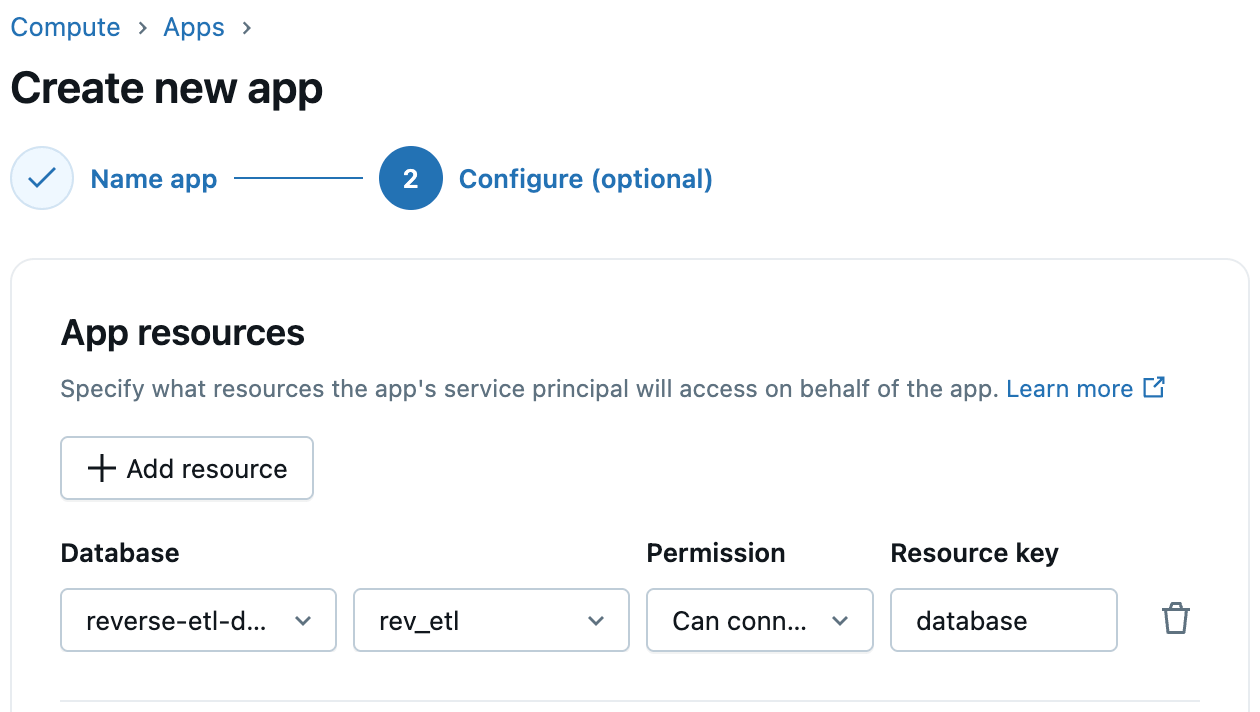
Step 3: Configure Lakebase Access in Databricks Apps
Databricks Apps support first-class integration with Lakebase. When creating your app, simply add Lakebase as an app resource and select the Lakebase instance and database. Databricks automatically provisions a corresponding Postgres role for the app’s service principal, streamlining app-to-database connectivity. You can then grant this role the required database, schema, and table permissions.
Step 4: Deploy Your App Code
With your data synced and permissions in place, you can now deploy the Flask app that powers the support portal. The app connects to Lakebase via Postgres and serves a rich dashboard with charts, filters, and interactivity.
Conclusion
Bringing analytical insights into operational applications no longer needs to be a complex, brittle process. With Lakebase, reverse ETL becomes a fully managed and integrated capability. It combines the performance of a Postgres engine, the reliability of a scalable architecture, and the governance of the Databricks Platform.
Whether you are powering an intelligent support portal or building other real-time, data-driven experiences, Lakebase reduces engineering overhead and speeds up the path from insight to action.
To learn more about how to create synced tables in Lakebase, check out our documentation and get started today.