Lambda Architecture
What is Lambda Architecture?
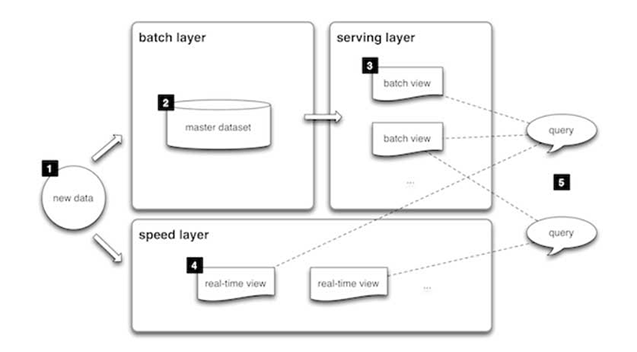
Lambda architecture is a way of processing massive quantities of data (i.e. "Big Data") that provides access to batch-processing and stream-processing methods with a hybrid approach. Lambda architecture is used to solve the problem of computing arbitrary functions. The lambda architecture itself is composed of 3 layers:
Here’s more to explore
Batch Layer
New data comes continuously, as a feed to the data system. It gets fed to the batch layer and the speed layer simultaneously. It looks at all the data at once and eventually corrects the data in the stream layer. Here we can find lots of ETL and a traditional data warehouse. This layer is built using a predefined schedule, usually once or twice a day. The batch layer has two very important functions:
- To manage the master dataset
- To pre-compute the batch views.
Serving Layer
The outputs from the batch layer in the form of batch views and those coming from the speed layer in the form of near real-time views get forwarded to the serving. This layer indexes the batch views so that they can be queried in low-latency on an ad-hoc basis.
Speed Layer (Stream Layer)
This layer handles the data that are not already delivered in the batch view due to the latency of the batch layer. In addition, it only deals with recent data in order to provide a complete view of the data to the user by creating real-time views.
Benefits of lambda architectures
Here are the main benefits of lambda architectures:
- No Server Management – you do not have to install, maintain, or administer any software.
- Flexible Scaling – your application can be either automatically scaled or scaled by the adjustment of its capacity
- Automated High Availability – refers to the fact that serverless applications have already built-in availability and faults tolerance. It represents a guarantee that all requests will get a response about whether they were successful or not.
- Business Agility – React in real-time to changing business/market scenarios
Challenges with lambda architectures
- Complexity – lambda architectures can be highly complex. Administrators must typically maintain two separate code bases for batch and streaming layers, which can make debugging difficult.