Data Orchestration
What is data orchestration?
Orchestration is the coordination and management of multiple computer systems, applications and/or services, stringing together multiple tasks in order to execute a larger workflow or process. More specifically, orchestration is the coordinated execution of multiple IT automation tasks or processes across multiple computer systems, applications and services. These processes can consist of multiple tasks that are automated and can involve multiple systems.
The goal of orchestration is to streamline and optimize the execution of frequent, repeatable processes to help data teams more easily manage complex tasks and workflows. Anytime a process is repeatable, and its tasks can be automated, orchestration can be used to save time, increase efficiency and eliminate redundancies. For example, you can simplify data and machine learning pipelines with jobs orchestration.
Here’s more to explore
Key benefits of orchestration
Orchestration delivers significant advantages for IT, data and AI teams and organizations:
- Standardization: Orchestration establishes consistent processes and workflows across the entire IT infrastructure, reducing variability and errors
- Improved collaboration: By creating unified workflows that span multiple systems and teams, orchestration breaks down silos and enables better cross-functional collaboration
- Enhanced scalability: IT teams can scale operations more efficiently by replicating and adapting orchestrated workflows rather than manually re-creating processes
- Enterprise-wide automation: Orchestration allows IT teams to build fully automated workflows that span entire enterprise use cases, connecting disparate systems into cohesive end-to-end processes
- Security and consistency: Enhanced security is achieved through orchestration by applying security policies and standards consistently across all cloud environments and infrastructure
- Auditability and observability: Orchestration can maintain an auditable record of each step and workflow execution across various inputs and triggers. This detailed logging aids in compliance, troubleshooting and performance optimization.
What is the difference between process automation and process orchestration?
While automation and orchestration are highly complementary, they mean different things.
- Automation — Programming a task to be executed without the need for human intervention. It focuses on streamlining individual, repetitive tasks to eliminate manual work and reduce errors.
- Orchestration — The configuration of multiple tasks (some may be automated) into one complete end-to-end process or job. Orchestration software also needs to react to events or activities throughout the process and make decisions based on outputs from one automated task to determine and coordinate the next tasks.
Automation vs. orchestration: When to use each
While automation and orchestration are highly complementary, they serve distinct purposes in IT operations.
When to use automation
Automation is ideal for executing single, repetitive tasks that don’t require coordination with other processes like data backups, email notifications or file transfers.
When to use orchestration
Orchestration becomes essential when you need to:
- Coordinate multiple automated tasks into a cohesive workflow
- Manage dependencies between different systems and processes
- Build enterprise-wide workflows that span multiple teams or cloud environments
- React dynamically to events and make decisions based on intermediate outputs
- Maintain visibility and auditability across complex, multistep processes
The relationship between automation and orchestration
Think of automation as the building blocks and orchestration as the blueprint. You can maximize efficiency by automating numerous functions, but orchestration ensures those functions work together harmoniously. Orchestration takes your individual automated tasks and weaves them into intelligent, end-to-end workflows that drive business outcomes.
What is application orchestration?
Application orchestration is the integration of two or more software applications. You might do this to automate a process or to enable real-time syncing of data. Most software development efforts need some kind of application orchestration — without it, you’ll find it much harder to scale application development, data analytics, machine learning and AI projects.
The application orchestration process allows you to manage and monitor your integrations centrally and add capabilities for message routing, security, transformation and reliability. This approach is more effective than point-to-point integration because the integration logic is decoupled from the applications themselves and is managed within a container instead.
What is service orchestration?
Service orchestration works in a similar way to application orchestration. It allows you to coordinate and manage systems across multiple cloud vendors and domains, which is essential in today’s world. The approach covers microservice orchestration, network orchestration and workflow orchestration.
Individual services lack the native capacity to integrate with one another, and each has its own dependencies and demands. The more complex the system, the more important it is to orchestrate the various components. That way, you can scale infrastructures as needed, optimize systems for business objectives and avoid service delivery failures.
What is container orchestration?
Container orchestration is the automation of container management and coordination. Software teams use container orchestration tools like Kubernetes and Docker Swarm to control and automate tasks such as provisioning and deployments of containers, allocation of resources between containers, health monitoring of containers and securing interactions between containers.
How does container orchestration work?
Software orchestration teams start by describing an app’s configuration in a file, which tells the container orchestration tool where to gather container images and how to network between containers.
The tool also schedules deployment of containers into clusters and identifies the most appropriate host based on pre-set constraints such as labels or metadata. It then manages the container’s lifecycle based on the specifications laid out in the file.
Automating container orchestration enables you to scale applications with a single command, quickly create new containerized applications to handle growing traffic and simplify the installation process. It also improves security.
What is cloud orchestration?
Cloud orchestration is the process of automating the tasks that manage connections on private and public clouds. It also integrates automated tasks and processes into a workflow to help you perform specific business functions.
The rise of cloud computing — involving public, private and hybrid clouds — has led to increasing complexity, creating a need for cloud orchestration software that can manage and deploy multiple dependencies across multiple clouds. Cloud service orchestration includes tasks such as provisioning server workloads and storage capacity, and orchestrating services, workloads and resources.
Cloud orchestration and automation are two different things: Cloud orchestration focuses on the entirety of IT processes, while automation focuses on an individual piece of the process. Orchestration simplifies automation across a multicloud environment, while ensuring that policies and security protocols are maintained.
Orchestration in multicloud and hybrid environments
As organizations increasingly adopt multicloud and hybrid cloud strategies, orchestration has become essential for managing complexity across diverse infrastructure.
The challenge of multicloud complexity
Modern enterprises often use a combination of public clouds (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud), private clouds and on-premises systems. Without orchestration, managing workloads, data flows and services across these disparate environments becomes fragmented and error-prone.
Key benefits for multicloud environments
- Unified management: Orchestration provides a single control plane to manage resources across all cloud platforms and on-premises systems
- Consistent policies: Enhanced security and consistency are achieved through orchestration by applying security policies and standards consistently across all cloud environments
- Flexibility and portability: Orchestrated workflows can adapt to different cloud providers, reducing vendor lock-in
- Optimized resource allocation: Automatically distribute workloads based on cost, performance and availability across multiple clouds
In the cloud, an orchestration layer manages interactions and interconnections between cloud-based and on-premises components. These include servers, networking, virtual machines, security and storage, ensuring seamless operations regardless of where your resources reside.
What is security orchestration?
Security orchestration ensures your automated security tools can work together effectively and streamlines the way they’re used by security teams. With security orchestration, the tools can communicate with each other and share data — reducing the potential for human error, allowing teams to respond better to threats and saving time and cost through data automation.
Security orchestration, automation and response (SOAR) is an approach that combines automation and orchestration, and allows organizations to automate threat-hunting, the collection of threat intelligence and incident responses to lower-level threats.
SOAR refers to three software capabilities as defined by Gartner:
- Orchestration — Threat and vulnerability management
- Automation — Security operations automation
- Response — Security incident response
What is an orchestration layer?
An orchestration layer is required if you need to coordinate multiple API services. It enables you to create connections or instructions between your connector and those of third-party applications. This effectively creates a single API that makes multiple calls to multiple different services in response to a single API request.
It also manages data formatting between separate services, where requests and responses need to be split, merged or routed. By adding this abstraction layer, you provide your API with a level of intelligence for communication between services. An orchestration layer assists with data transformation, server management, handling authentications and integrating legacy systems.
In the cloud, an orchestration layer manages interactions and interconnections between cloud-based and on-premises components. These include servers, networking, virtual machines, security and storage.
What is journey orchestration?
Journey orchestration takes the concept of customer journey mapping a stage further. It uses automation to personalize journeys in real time, rather than relying on historical data. The goal remains to create and shape the ideal customer journey.
Journey orchestration also enables businesses to be agile, adapting to changes and spotting potential problems before they happen.
Orchestration in practice
The following are practical examples of how different sectors leverage orchestration.
Financial services
Financial institutions use orchestration to manage fraud detection pipelines, processing transaction data in real time across multiple systems. Orchestrated workflows automatically flag suspicious activities, trigger verification processes and update risk models while maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements and audit trails.
Healthcare
Healthcare organizations orchestrate patient data flows between electronic health records (EHR), lab systems, imaging platforms and billing systems. For example, when a patient visits multiple departments, orchestration ensures that test results, diagnoses and treatment plans are synchronized across all systems, enabling coordinated care while maintaining HIPAA compliance.
e-Commerce and retail
Retailers use orchestration to manage inventory, pricing and customer data across online stores, physical locations and third-party marketplaces. Orchestrated workflows automatically update stock levels, trigger reorder processes, adjust pricing based on demand and personalize customer recommendations in real time.
Manufacturing and supply chain
Manufacturers orchestrate workflows that connect IoT sensors, production systems, quality control and logistics platforms. Orchestration enables predictive maintenance by coordinating data from equipment sensors, triggering maintenance workflows before failures occur and automatically adjusting production schedules.
Media and entertainment
Streaming platforms use orchestration to manage content delivery pipelines, from ingestion and transcoding to distribution across global content delivery networks (CDNs). Orchestrated workflows ensure content is processed, optimized for different devices and delivered with minimal latency.
Telecommunications
Telecom providers orchestrate network functions, service provisioning and customer onboarding processes. When a new customer signs up, orchestration coordinates identity verification, service activation, billing setup and network configuration across multiple back-end systems.
Orchestration tools
The orchestration needed for complex tasks requires heavy lifting from data teams and specialized tools to develop, manage, monitor and reliably run such pipelines. Typically, orchestration tools are separate from the actual data or machine learning tasks. This lack of integration leads to fragmentation of efforts across the enterprise, requiring users to frequently switch contexts.
As companies undertake more BI and AI initiatives, the need for simple, scalable and reliable orchestration tools has increased. A variety of tools exist to help teams unlock the full benefits of orchestration to automate workloads.
Service orchestration tools help you integrate different applications and systems, while cloud orchestration tools bring together multiple cloud systems. Orchestration tools also help manage end-to-end processes from a single location and simplify process creation to create workflows that were otherwise unachievable.
For example, Databricks helps unify your data warehousing and AI use cases on a single platform. Learn more about orchestrating Databricks workloads.
What is application release orchestration?
Application release orchestration (ARO) enables DevOps teams to improve the quality, velocity and governance of new releases by automating application deployments, managing continuous integration and continuous delivery pipelines, and orchestrating release workflows.
As well as deployment automation and pipeline management, application release orchestration tools also enable enterprises to scale release activities across multiple diverse teams, technologies, methodologies and pipelines. Some well-known ARO tools include GitLab, Microsoft Azure Pipelines and FlexDeploy.
What is process orchestration?
While automated processes are necessary for effective orchestration, using different tools for each individual task (and sourcing them from multiple vendors) can lead to silos.
Process orchestration involves unifying individual tasks into end-to-end processes and streamlining system integrations with universal connectors, direct integrations or API adapters. IT teams can then manage the entire process lifecycle from a single location.
Benefits include reducing complexity by coordinating and consolidating disparate tools, improving mean time to resolution (MTTR) by centralizing the monitoring and logging of processes, and integrating new tools and technologies with a single orchestration platform.
This type of software orchestration makes it possible to rapidly integrate virtually any tool or technology.
The purpose of data orchestration platforms
Data orchestration is an automated process for taking siloed data from multiple storage locations, combining and organizing it, and making it available for analysis. The process connects all your data centers, whether they’re legacy systems, cloud-based tools or data lakes. The data is transformed into a standard format, so it’s easier to understand and use in decision-making.
Most companies accumulate a vast amount of data, which is why automated tools are necessary to organize it. Big data orchestration is the process of organizing data that’s too large, fast or complex to handle with traditional methods. Data orchestration also identifies “dark data,” which is information that takes up space on a server but is never used.
Data orchestration platforms are ideal for ensuring compliance and spotting problems. For example, a payment orchestration platform gives you access to customer data in real time, so you can see any risky transactions.
What is DevOps orchestration?
DevOps orchestration is the coordination of your entire company’s DevOps practices and the automation tools you use to complete them. The aim is to minimize production issues and reduce the time it takes to get new releases to market.
Orchestrating your automated tasks helps maximize the potential of your automation tools. This brings us back to the orchestration vs. automation question: You can maximize efficiency by automating numerous functions to run at the same time, but orchestration is needed to ensure those functions work together.
For example, DevOps orchestration for a cloud-based deployment pipeline enables you to combine development, QA and production.
What is Docker orchestration?
Docker is a user-friendly container runtime that provides a set of tools for developing containerized applications. It allows you to package your code into an image, which is then used to create a container. Docker orchestration is a set of practices and technologies for managing Docker containers.
This type of container orchestration is necessary when your containerized applications scale to a large number of containers. Docker orchestration is used for tasks like provisioning containers, scaling up and down, managing networking and load balancing.
The Docker ecosystem offers several tools for orchestration, such as Swarm. Kubernetes is commonly used to orchestrate Docker containers. Cloud container platforms also provide basic orchestration capabilities.
AI-powered orchestration
AI is transforming orchestration by adding intelligent decision-making, predictive capabilities and adaptive optimization to automated workflows.
AI enhances orchestration
Traditional orchestration follows predefined rules and sequences. AI-powered orchestration goes further by learning from historical data, predicting outcomes and adjusting workflows based on real-time conditions. This enables orchestration systems to become more autonomous, efficient and resilient.
Key capabilities of AI-powered orchestration
- Predictive workflow optimization: AI analyzes past workflow executions to predict bottlenecks, resource needs and potential failures before they occur, automatically adjusting resource allocation and task scheduling
- Intelligent error handling: Instead of simply retrying failed tasks, AI-powered orchestration can diagnose root causes, suggest remediation strategies and automatically route workflows through alternative paths
- Anomaly detection: Machine learning models continuously monitor orchestrated workflows to detect unusual patterns, performance degradation or security threats in real time
- Adaptive resource management: AI dynamically allocates computational resources based on predicted workload demands, optimizing costs while maintaining performance
- Natural language interfaces: AI enables users to create, modify and monitor orchestration workflows using conversational interfaces, making orchestration more accessible to nontechnical users
AI/ML pipeline orchestration
AI-powered orchestration is particularly valuable for managing machine learning pipelines, where it can automate model training, testing, deployment and retraining cycles based on model performance metrics and data drift detection.
Common orchestration pitfalls and how to avoid them
While orchestration offers significant benefits, organizations often encounter challenges during implementation. Here are some common pitfalls and how to avoid them:
- Overorchestrating simple processes — Applying orchestration to simple tasks adds unnecessary complexity. Start with processes that genuinely involve multiple systems and dependencies. Simple, single-task automations may not need full orchestration.
- Insufficient error handling and monitoring — Orchestrated workflows can fail silently without proper monitoring. Build comprehensive error handling into every workflow step and implement robust alerting systems. Orchestration keeps detailed logs of workflows, which aid in auditability and observability.
- Creating tightly coupled dependencies — Rigid dependencies make workflows fragile and difficult to modify. Design loosely coupled workflows with modular, reusable components. Implement retry logic, fallback mechanisms and graceful degradation strategies.
- Neglecting documentation and governance — As workflows proliferate, teams lose track of what exists and who owns which processes. Maintain clear documentation of all orchestrated workflows, including data lineage and system dependencies. Orchestration can maintain an auditable record of each step and workflow execution. You can use this to enforce accountability.
- Ignoring security and compliance — Orchestration workflows often handle sensitive data across multiple systems. Apply security policies and standards consistently across all orchestrated environments. Implement proper authentication, authorization and encryption while maintaining audit trails for compliance.
Orchestrating data and machine learning pipelines on the Databricks Data Intelligence Platform
The Databricks Platform makes it easy to orchestrate multiple tasks so you can effortlessly build data and machine learning workflows.
Orchestrating multistep tasks makes it simple to define data and ML pipelines using interdependent, modular tasks consisting of notebooks, Python scripts and JARs. Data teams can easily create and manage multistep pipelines that transform and refine data, and train machine learning algorithms, all within the familiar workspace of the Databricks Platform, saving teams immense time, effort and context switches.
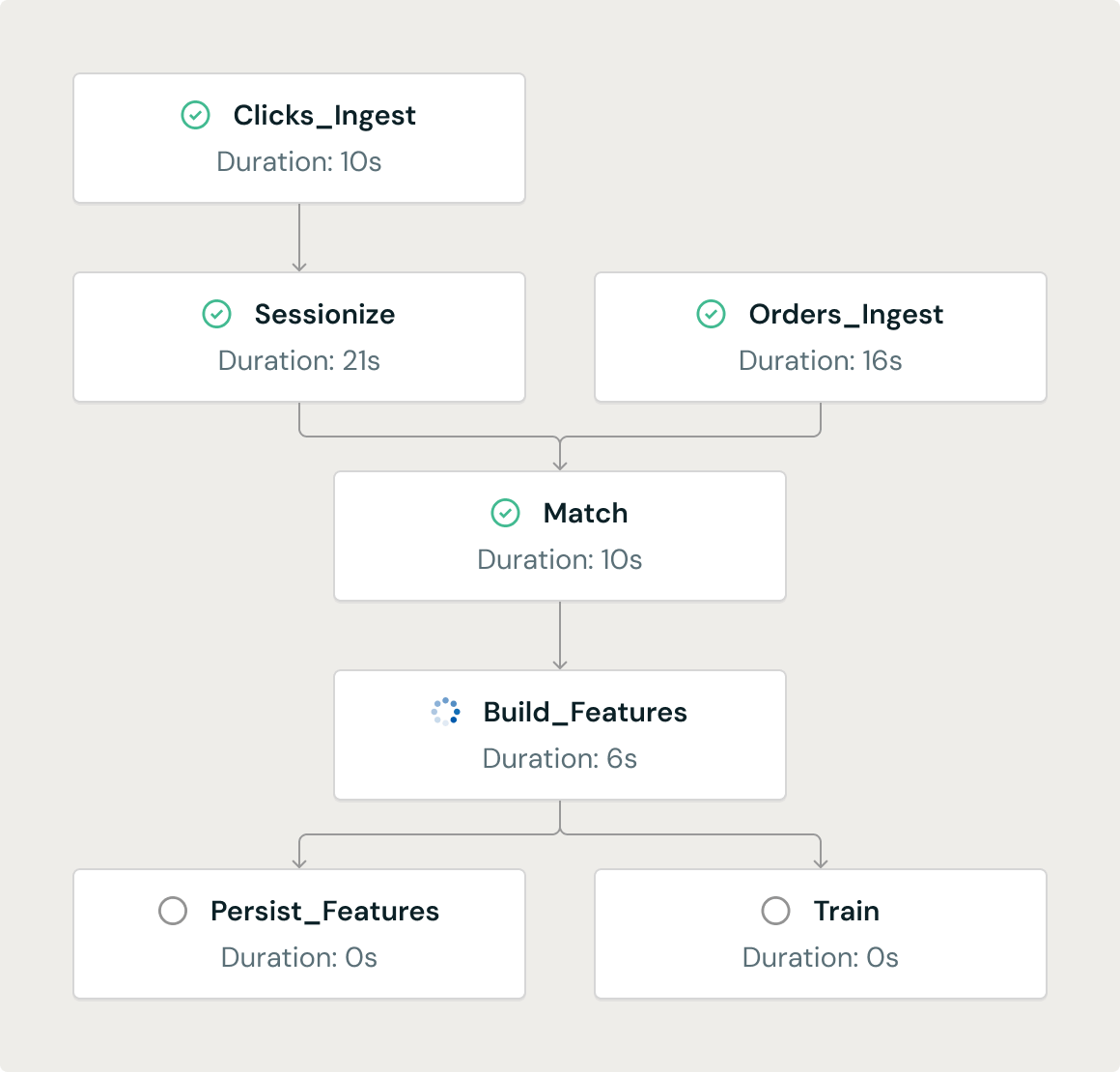
In the example above, a job consisting of multiple tasks uses two tasks to ingest data: Clicks_Ingest and Orders_Ingest. This ingested data is then aggregated and filtered in the “Match” task, from which new machine learning features are generated (Build_Features), persistent (Persist_Features) and used to train new models (Train).
Jobs orchestration is fully integrated in the Databricks Platform and requires no additional infrastructure or DevOps resources. Customers can use the Jobs API or UI to create and manage jobs and features, such as email alerts for monitoring.
Your data team doesn’t have to learn new skills to benefit from this feature. Lakeflow Jobs also enables you to orchestrate anything that has an API outside of the Databricks Platform and across all clouds, e.g., pull data from CRMs. You can enable Lakeflow Jobs for your workspace in AWS, Azure and GCP.
FAQ
How much does orchestration software cost?
Orchestration software costs vary widely depending on the platform and scale. Open source tools like Apache Airflow are free but require infrastructure and maintenance costs. Cloud-based platforms typically charge based on workflow executions, data volume or compute resources, ranging from hundreds to thousands of dollars per month.
When evaluating costs, consider licensing fees, infrastructure requirements, implementation time and training needs. Many vendors offer free tiers or trials. Remember that the total cost should be weighed against the efficiency gains and cost savings achieved through automation.
What skills are required for orchestration?
Core skills for orchestration include:
- Programming: Familiarity with Python, SQL or Bash for workflow logic
- Data pipeline knowledge: Understanding of ETL processes and data integration
- Systems architecture: Knowledge of how systems, APIs and cloud services interact
- DevOps practices: Experience with CI/CD, version control and infrastructure as code
Your data team doesn’t have to learn extensive new skills to benefit from orchestration. Many modern platforms offer user-friendly interfaces, visual workflow builders and pre-built templates that reduce technical barriers.
Which orchestration tool should I choose?
Choosing the right tool depends on your specific needs. Consider the following:
- Use case alignment: Match the tool to your primary needs — data pipelines, application deployment or cloud infrastructure
- Scalability: Ensure the platform can handle current and future volumes
- Integration capabilities: Verify compatibility with your existing systems
- Ease of use: Balance code-based flexibility with visual workflow designers
- Cost structure: Assess whether pricing aligns with your budget