A Practical AI Governance Framework for Enterprises
A comprehensive guide to implementing AI governance tools and programs responsibly and effectively
Summary
- For organizations looking to develop and document rigorous AI governance, we've developed an AI governance framework that outlines a structured approach to responsible AI development.
- AI governance best practices, including risk management, legal compliance, ethical oversight, and operational monitoring, are key to supporting transparent, accountable AI systems.
- The AI governance framework is intended to help enterprises scale AI programs while managing regulatory expectations, reducing risk, and maintaining stakeholder trust.
As organizations embrace AI at scale, the need for formal governance grows. Enterprises must align AI development with business goals, meet legal obligations, and account for ethical risks.
We’ve introduced the Databricks AI Governance Framework to provide a structured and practical approach to governing AI adoption across the enterprise. This framework is designed to support AI governance program development, deployment, and continuous improvement.
Introduction to AI Governance
The term "AI governance" refers to the kind of structures, processes, and oversight that AI systems require in order to be responsibly developed and deployed across an enterprise. As organizations scale generative AI, governance becomes a foundational principle for issues such as aligning AI initiatives with business objectives, managing ethical and regulatory obligations, and confirming that models behave consistently and predictably while in production.
Additionally, AI governance has a significant impact on AI ROI. Without clear ownership, policies, and risk controls, AI programs can frequently stall, encounter avoidable security incidents, or they might altogether fail to earn stakeholder trust. Industry research shows that governance challenges are a primary barrier to scaling AI, while more than half of leaders point to unclear ownership, inadequate risk controls, or lack of compliance as root causes of failed AI projects. Moreover, issues like model bias, data leakage, and unauthorized model behavior have been on the rise, prompting the need for stronger governance practices. These figures highlight just how governance is a crucial prerequisite to AI value, not just an afterthought.
It's also important to distinguish governance from security. While security focuses on protecting data, models, and infrastructure from threats, governance instead defines how decisions are made about AI development and use of AI.
This includes issues like establishing accountability, setting policies, evaluating risks, and ensuring ethical and transparent operations. Together, governance and security form the foundation for safe, scalable AI. With the Databricks AI Governance Framework, enterprises gain a structured approach to building these capabilities before scaling AI across products and workflows.
Why AI governance can’t wait
According to a 2024 global survey of 1,100 technology executives and engineers conducted by Economist Impact, 40% of respondents believed that their organization’s AI Governance program was insufficient in ensuring the safety and compliance of their AI assets and use cases. In addition, data privacy and security breaches were the top concern for 53% of enterprise architects, while security and governance are the most challenging aspects of data engineering for engineers.
In addition, according to Gartner, AI trust, risk, and security management is the #1 top strategy trend in 2024 that will factor into business and technology decisions, and by 2026, AI models from organizations that operationalize AI transparency, trust, and security will achieve 50% increase in terms of adoption, business goals, and user acceptance.
It is evident that the lack of enterprise-level AI governance programs is fast becoming a key blocker to realizing return on value from AI investments and AI adoption as a whole.
So we developed a comprehensive guidance framework that enterprises can leverage to build effective AI governance programs.
A Structured Approach to AI Governance
Best practices for implementing AI governance require a structured, repeatable methodology that aligns people, processes, and technology across the organization. The Databricks AI Governance Framework develops a holistic approach that begins with establishing clear business objectives, defining ownership, and creating governance models that integrate seamlessly with existing enterprise structures. Governance programs succeed when they are treated as extensions of existing organizational strategies, risk practices, and data management processes.
A key aspect of this approach is embedding governance responsibilities across teams rather than centralizing them with a single group. Business leaders set the strategic direction by articulating AI goals, defining acceptable risk levels, and ensuring alignment with enterprise priorities.
Teams such as data engineering, data science and ML engineering operationalize these directives by implementing standards for data quality, model documentation, lineage, reproducibility, and access controls. Legal, compliance, and security teams play an additional, parallel role to ensure regulatory readiness, policy adherence, and data protection of data and model assets throughout the lifecycle.
Integrating governance with operational systems provides both consistency and scalability. For example, unified data governance solutions like Unity Catalog can standardize access policies, enforce lineage, and centralize metadata for risk assessment and auditability. Meanwhile, strong data engineering practices ensure that AI programs are built on reliable, well-governed data foundations, with reproducible pipelines and transparent transformations that can be monitored over time.
Effective AI governance is not a one-time exercise. Ongoing monitoring and evaluation processes are required to track model performance, assess data drift, detect bias, confirm policy compliance, and identify emerging risks. This continuous feedback loop ensures that models remain aligned with business expectations and regulatory requirements as conditions evolve. Regular reviews by cross-functional teams also help organizations proactively adjust policies, retrain models, and refine governance processes.
By taking a structured, collaborative, and lifecycle-oriented approach, organizations can build governance programs that scale reliably, reduce risk, and accelerate the safe adoption of AI across the enterprise.
The five foundational pillars for AI governance
In this framework, we introduce 43 key considerations that are essential for every enterprise to understand (and implement as appropriate) to effectively govern their AI journeys.
Key considerations for AI governance are logically grouped across five foundational pillars, designed and sequenced to reflect typical enterprise organizational structures and personas.
- AI organization
- Legal and regulatory compliance
- Ethics, transparency and interpretability
- Data, AI ops, and infrastructure
- AI security
Gartner®: Databricks Cloud Database Leader
A framework for AI governance
AI Organization
AI Organization embeds AI governance within the organization’s broader governance strategy. It underscores the foundation for an effective AI program through best practices like clearly defined business objectives and integrating the appropriate governance practices that oversee the organization's people, processes, technology, and data. It explains how organizations can establish the oversight required to achieve their strategic goals while reducing risk.
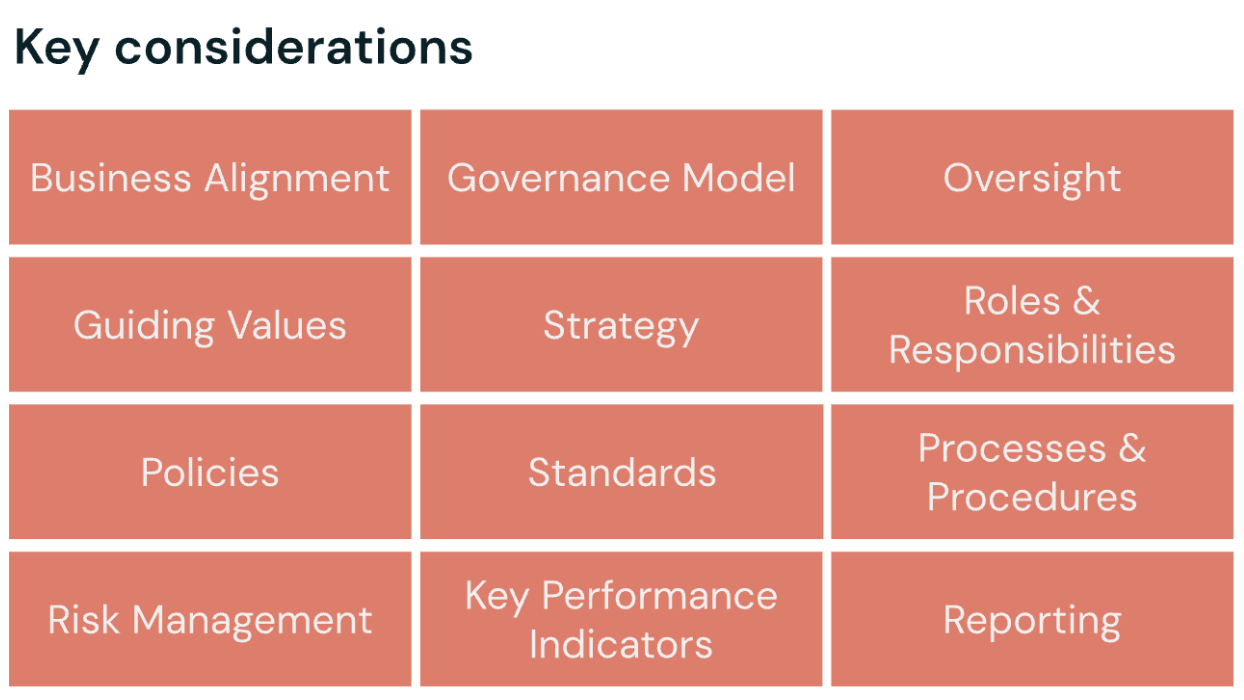
Key considerations for an effective AI governance organization
- Business alignment
- Governance model
- Oversight
- Guiding values
- Strategy
- Roles & responsibilities
- Policies
- Standards
- Processes & procedures
- Risk management
- Key performance indicators
- Reporting
Download the AI Governance Framework to get the steps for getting started.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance of AI Initiatives
The Legal and Regulatory Compliance pillar helps organizations align AI initiatives with applicable laws and regulations. It guides managing legal risks, interpreting sector-specific requirements, and adapting compliance strategies in response to evolving regulatory landscapes. The outcome is that AI programs are developed and deployed within a robust legal and regulatory framework.
Steps to align AI initiatives with laws and regulations
- Assess legal and regulatory considerations
- Prioritize liability and risk management
- Plan a comprehensive legal review
- Deploy legal protections and safeguards
- Monitor ongoing compliance and conduct regular audits
- Review emerging trends in AI ethics and regulation

Ethics, Transparency and Interpretability of AI Programs
In organizations building trustworthy and responsible AI systems, it’s important to adhere to ethical principles such as fairness, accountability, and human oversight while promoting explainability and stakeholder engagement. This pillar in the AI governance framework provides methods to establish accountability and structure within organizational teams, helping to ensure that AI decisions are interpretable, aligned with evolving ethical standards, and fostering long-term trust and societal acceptance.
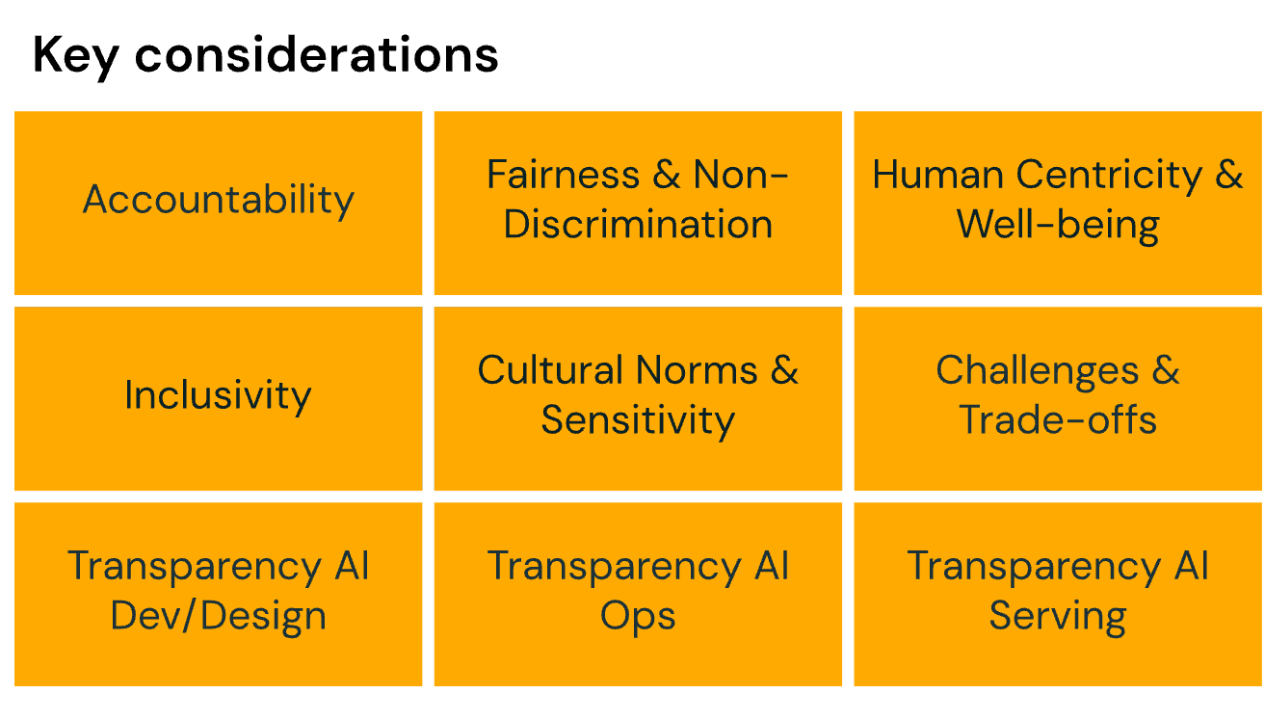
When designing AI programs and putting in place AI governance tools, consider how you will address:
- Accountability
- Fairness and non-discrimination
- Human centricity and well-being
- Inclusivity
- Cultural norms and sensitivity
- Challenges and trade-offs of all of the above
- Transparency in AI development and design
- Transparency in AI ops
- Transparency in AI serving
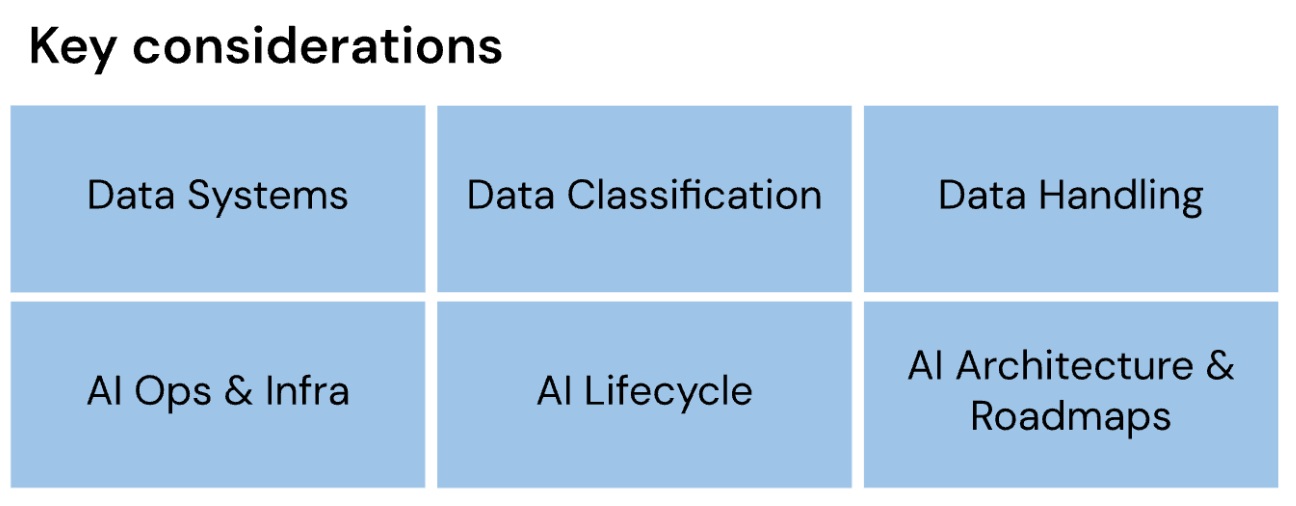
Data, AI Ops, and Infrastructure for AI Governance
The Data, AI Operations (AIOps), and Infrastructure pillar defines the foundation that supports organizations in fully deploying and maintaining AI. You’ll need guidelines for creating a scalable and reliable AI infrastructure, managing the machine learning lifecycle, and ensuring data quality, security, and compliance. This pillar also emphasizes best practices for AI operations, including model training, evaluation, deployment, and monitoring, so AI systems are reliable, efficient, and aligned with business goals.
Pillar V: AI Security
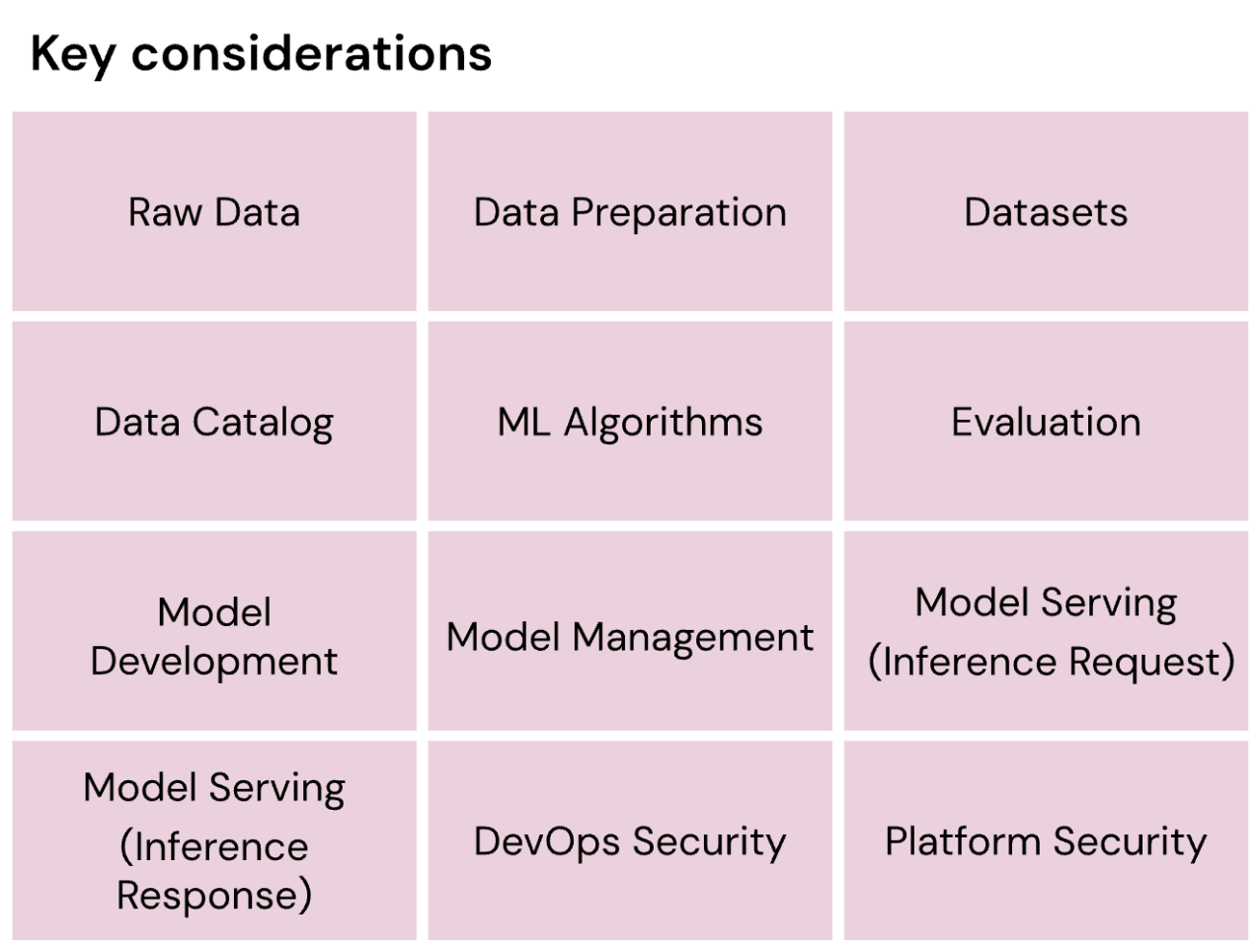
The AI Security pillar introduces the Databricks AI Security Framework (DASF), a comprehensive framework for understanding and mitigating security risks across the AI lifecycle. It covers critical areas such as data protection, model management, secure model serving, and the implementation of robust cybersecurity measures to protect AI assets.
Related: See an example walkthrough of how an organization can leverage the AI governance framework to create clear ownership and alignment across the AI program lifecycle. Watch this presentation made during the 2025 Data + AI Summit.
AI Governance Framework
The AI Governance Framework whitepaper is available for organizations looking to develop their own AI governance.
Please reach out to us via email at [email protected] for any questions or feedback. If you’re interested in contributing to future updates of this framework (and other upcoming artifacts) by joining our reviewer community, we’d love to hear from you as well!
Key Principles for Effective AI Governance
AI governance depends on a consistent set of foundational principles that operate across every stage of the AI lifecycle. These principles make sure AI systems are developed and deployed responsibly while also providing a necessary structure for organizations to meet regulatory expectations, maintain stakeholder trust and mitigate risk as adoption scales. Principles such as transparency, accountability, fairness, and human oversight lie at the core of any effective strategy.
Transparency begins with clear, accessible documentation of data sources, model assumptions, training methodologies and evaluation processes. A practice of transparency requires systematic tracking of lineage, versioning, and model behaviors so teams can trace how decisions are made and identify contributing factors when issues arise. Governance tools that centralize metadata, audit trails, and access policies support this work by making operational details visible and verifiable across teams.
AI governance should also prioritize accountability measures so that any AI system features clearly defined owners responsibility for outcomes, risk management, and adherence to governance standards. An effective accountability framework establishes roles across business, technical, legal, and compliance groups; distributes decision-making rights; and creates mechanisms for escalation when unexpected model behavior or ethical concerns arise. Additionally, creating KPIs and performance thresholds can give leaders measurable benchmarks for evaluating AI systems over time.
A principle of fairness requires proactively identifying and mitigating bias throughout data collection, model training, and production monitoring. Techniques such as disparate impact analysis, bias detection metrics, and representative sampling strategies can help teams understand how model outputs vary across user groups. Continuous fairness assessments allow organizations to identify drift or inequities as real world usage evolves.
Finally, human oversight helps AI systems align with organizational values and regulatory requirements. This step involves defining where human review is required, designing clear fallback procedures, and ensuring subject-matter experts can intervene when model outputs are ambiguous, high-risk, or sensitive. Oversight mechanisms should be integrated into both development workflows and production operations so that safeguards remain active throughout the AI lifecycle.
Implementing Responsible AI Practices
Responsible AI practices are the guardrails that make sure AI systems serve people, businesses, and society in ways that are safe, fair, and aligned with organizational values. Implementing these practices requires a holistic approach across the entire AI lifecycle. From data sourcing and model development to deployment, monitoring, and eventual retirement, each stage is an opportunity to embed safeguards. In short, the goal of any responsible AI practice is to reduce harm, strengthen trust, and improve system performance over time.
A critical component of responsible AI is aligning system behavior with human values and organizational principles. This begins with defining the intended use of a model – including any sensitive or high-impact scenarios – and establishing requirements related to privacy, fairness, security, and explainability. It is crucial to incorporate this criteria early in the design process so that teams explicitly address ethical considerations, rather than simply responding reactively. Specific techniques help AI systems operate consistently with user expectations and societal norms, such as model interpretability tools, representative training datasets, and human-in-the-loop review processes.
Additionally, risk identification and mitigation should be integrated directly into development workflows. Organizations must evaluate risks such as bias, model drift, hallucinations, data leakage, and unsafe outputs, and develop mitigation strategies tied to each. These strategies may also include differential privacy, prompt and output filtering, adversarial testing, and red-teaming exercises tailored to domain-specific risks. As this testing proceeds, teams should document risk assessments and controls in order to provide transparency and support regulatory and internal audit requirements.
Implementing responsible AI practices is an ongoing job. Even well-governed models can degrade as data distributions shift or new requirements emerge. Teams should establish automated monitoring pipelines to help them track performance metrics, fairness indicators, and policy compliance in production. When issues arise, retraining procedures, structured incident reviews, and updated documentation all ensure AI systems evolve responsibly.
It is important for any team to balance innovation with caution. Teams should create pathways that enable experimentation, such as sandbox environments or controlled pilot deployments, while maintaining guardrails that prevent unintended harm. This balance empowers organizations to explore new generative AI capabilities while adhering to governance expectations and ethical standards.
Getting Started with DAGF Implementation
Implementing the Databricks AI Governance Framework (DAGF) begins with a clear, practical roadmap that guides organizations from early planning to enterprise-scale operations. The first step is establishing foundational governance structures: defining roles and responsibilities, documenting AI use cases, and assessing organizational readiness across data quality, model development practices, and compliance requirements. This initial alignment ensures governance efforts directly support business priorities and risk tolerance.
A maturity model can help organizations evaluate where they stand today, and identify the next steps in their governance journey. For example, early-stage programs focus on documenting AI assets, centralizing access controls, and establishing baseline policies for data usage, model development, and review. As this matures, organizations can begin to introduce standardized workflows, automated lineage and monitoring, and cross-functional committees that oversee AI risk and compliance. Finally, fully mature programs operationalize governance across the lifecycle, which includes reproducible pipelines, continuous model evaluation, and well-defined processes for retraining, auditing, and incident response.
No matter how carefully a governance framework is implemented, there are some common pitfalls organizations face. For instance, many struggle when governance is treated as an afterthought or assigned to a single team without clear accountability. Others might underestimate the role of high-quality data, and fail to implement some foundational practices such as schema enforcement, lineage tracking, and controlled access. These gaps may seem minor on the surface, but they can create downstream challenges in transparency, reproducibility, and auditability. Establishing shared ownership across business, technical, and compliance teams, as well as grounding governance in strong data engineering practices, can help prevent this issue across an organization.
To gauge success, organizations should track progress and measure the impact of governance investments. Metrics may include reductions in model incidents and bias findings, improved model reproducibility, increased documentation completeness, shortened review cycles, faster approvals for new AI use cases, and higher adoption of standardized pipelines and tools. Over time, these indicators demonstrate how governance is an essential function for reliable, compliant, and operational efficiency.
Implementing governance should be a phased approach that helps organizations carefully align with their resources and goals. Many begin with high-impact use cases, applying governance controls to the most sensitive or business-critical models before expanding to broader programs. However, iterating and scaling incrementally can help organizations build a durable governance foundation that supports safe, transparent, and trusted AI adoption across the organization.
Why Databricks is leading this effort
As an industry leader in the data and AI space, with over 15,000 customers across diverse geographies and market segments, Databricks has continued to deliver on its commitment to principles of responsible development and open source innovation. We’ve upheld these commitments through our:
- Engagement with both industry and government efforts to promote innovation and advocate for the use of safe and trustworthy AI
- Interactive workshops to educate organizations on how to successfully shepherd their AI journey in a risk-conscious manner
- Open sourcing of key governance innovations such as MLFlow and Unity Catalog, the industry’s only unified solution for data and AI governance across clouds, data formats and data platforms.
These programs have offered us unique visibility into practical problems that enterprises and regulators face today in AI governance. In furthering our commitment to helping every enterprise succeed and accelerate their Data and AI journey, we decided to leverage this visibility to build (and make freely available) a comprehensive, structured and actionable AI Governance Framework.
Never miss a Databricks post
What's next?

Data Science and ML
June 12, 2024/8 min read
Mosaic AI: Build and Deploy Production-quality AI Agent Systems
AI
January 7, 2025/6 min read