AI Risk Management: A Comprehensive Guide to Securing AI Systems
Summary
- AI risk management provides a structured, lifecycle-wide approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating security, operational, compliance/ethical, and data risks introduced by AI systems, including generative AI.
- Effective programs combine regulatory alignment (e.g., EU AI Act, NIST AI RMF, USAISI guidance) with strong data governance, clear roles and accountability, continuous monitoring (including the “30% rule”), and practical controls over data, models, deployment, and access.
- Organizations that succeed treat AI as both a risk and a tool: they ground controls in frameworks like the Databricks AI Security Framework, use AI to enhance threat detection and compliance, and foster cross-functional collaboration so they can balance innovation with security, privacy, and trust.
As business leaders look to leverage AI technologies in their operations to drive efficiencies and innovation, they often struggle to understand their unique risk profile and the steps needed to manage AI risk effectively. The rapid adoption of AI systems across industries has created unprecedented opportunities, but it has also introduced complex challenges that require comprehensive AI risk management strategies.
Just like existing data resources, AI systems have cybersecurity, privacy, and regulatory compliance vulnerabilities, but they also introduce ethical concerns and unintended consequences such as bias, discrimination and lack of trust. Organizations implementing AI technologies must develop robust risk management approaches that address both traditional IT security concerns and the unique risks associated with artificial intelligence systems.
The complexity of AI risk management stems from multiple factors: the opacity of complex AI models, the scale of training data required, the speed of AI development, and the evolving landscape of regulatory compliance requirements including the EU AI Act. AI risks can manifest at any stage of the AI lifecycle, from initial data collection through AI deployment and ongoing operations.
Without proper access controls, AI systems can be exploited by bad actors leading to data breaches and model manipulation. Internal users may perform shadow AI and use generative AI models to find confidential data they shouldn't have access to. And without auditability and traceability of AI models and their data, organizations face non-compliance risks associated with AI.
In Cisco's 2024 Data Privacy Benchmark Study, 91% of organizations recognize they need to do more to reassure their customers that their data is being used only for intended and legitimate purposes in AI. But they are often at a loss to know what "more" means.
With many potential AI applications touching employees, customers, and partners, AI risk management accountability extends beyond IT. Without an understanding of how the components of an AI system work together and the ability to identify potential risks and mitigate risks present in their use cases, organizations can default to a worst-case approach and get bogged down trying to solve for all possible threats. They need a simplified way to manage AI risk while staying aligned with business priorities. That requires a common language and collaboration among business, data, AI, governance and security teams to navigate this balancing act and innovate without conflict.
Understanding AI Risk Management Frameworks and Strategies
Knowing that AI security threats cannot be viewed through the lens of security standards put in place for a deterministic pre-AI world, several AI risk management frameworks have sprung up to help galvanize organizations to address risks and protect their data effectively.
Common AI security frameworks such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Artificial Intelligence Risk Management Framework (AI RMF) effectively outline the risks associated with securing AI systems and provide a structured approach for risk identification and risk assessment, but stop short of fully describing how to apply the necessary controls and mitigations for each type of AI risk.
What is the AI Risk Management Strategy?
An effective AI risk management strategy involves implementing comprehensive risk management practices throughout the AI lifecycle. Organizations need risk management frameworks that address potential risks across AI development, deployment, and operations. The management framework AI RMF provides guidance on managing risks through risk mitigation strategies and practical risk management approaches.
What are the 4 Types of AI Risk?
AI risks can be categorized into four primary types:
Security risks: Including AI security threats, cyber threats, and security vulnerabilities that expose AI systems to attacks
Operational risks: Covering system failures, model drift, and performance degradation of AI models
Compliance and ethical risks: Addressing regulatory compliance, ethical implications, and unfair outcomes from AI systems
Data risks: Involving data quality, data integrity, sensitive data protection, and biased training data
To demystify the management of AI risks, the Databricks AI Security Framework (DASF) provides an actionable roadmap with guidelines for using defensive control recommendations while staying aligned with business priorities. DASF maps its risk management framework AI controls to 10 industry standards and frameworks and takes a holistic approach to awareness and mitigation for data and AI development teams to collaborate with security teams across their AI and machine learning lifecycle.
Understanding AI Compliance and Security Requirements
AI deployment also brings a crucial regulatory dimension to risk management, emphasizing the need for thoughtful oversight and responsible AI governance. Depending on the industry and location, organizations need to ensure regulatory compliance with a multitude of regulations including the EU AI Act and other emerging risks from new legislation.
The EU AI Act represents a landmark regulatory framework that classifies AI systems based on risk levels and imposes specific requirements for high-risk AI applications. Organizations deploying AI systems in Europe must understand these requirements and implement appropriate risk management frameworks to ensure regulatory compliance. Similar regulations are emerging globally, creating a complex landscape for AI governance.
Key compliance issues for AI systems involve data quality and reliability, AI security, resiliency, accountability and transparency, data privacy, and fairness and bias in AI models. Organizations must address these compliance requirements through comprehensive AI risk management practices that span the entire AI lifecycle.
AI governance frameworks should encompass policies, procedures, and controls that ensure responsible AI development and AI deployment. This includes establishing clear accountability structures, defining risk tolerance levels, implementing risk identification processes, and maintaining continuous monitoring of AI systems performance. Effective AI risk management requires collaboration between data scientists, engineers, security teams, and business stakeholders to balance innovation with risk management.
It starts with data governance, which results in better regulatory compliance with requirements such as HIPAA, FedRAMP, GDPR or CCPA. Data governance is crucial to ensure data quality, consistency, regulatory compliance, and internal organizational policies as well as data integrity, AI security, data privacy, auditing and risk management. Proper data governance helps prevent issues with biased training data and ensures input data meets quality standards.
For regulatory compliance, organizations need visibility to ensure discoverability and the ability to catalog data from various sources used in dual-use foundation models. This includes tracking historical data sources, monitoring data collection practices, and protecting sensitive data and sensitive personal data throughout the AI system development process. Housed within NIST, the recently formed U.S. AI Safety Institute (USAISI) will create guidelines for mechanisms for assessing AI risk and develop technical guidance that regulators will use on issues such as establishing thresholds for categorizing powerful models, authenticating content, watermarking AI-generated content, identifying and mitigating algorithmic discrimination, ensuring transparency, and enabling adoption of privacy-preserving AI.
Organizations leading in their use of AI are using AI tools to address risks in common operations challenges and systematic issues such as regulatory compliance change management, reducing false positives, fraud and AML prevention and addressing human error. They automate the monitoring of their AI systems to ensure high-quality training data and fair, unbiased machine learning models through continuous monitoring of AI system's performance.
Can AI Do Risk Management?
Yes, AI technologies can significantly enhance risk management capabilities across organizations. AI applications can assist risk management by identifying potential risks, conducting regular risk assessments, and developing risk mitigation strategies that adapt to changing threat landscapes. Machine learning algorithms can detect patterns and anomalies that humans might miss, making AI risk management more effective through continuous monitoring and automated risk assessment processes.
AI tools excel at processing vast amounts of historical data to identify potential risks before they materialize. Through predictive analytics and pattern recognition, AI systems can flag security vulnerabilities, detect cyber threats, and alert security teams to emerging risks in real-time. This proactive approach to risk management enables organizations to mitigate risks before they impact operations or compromise sensitive information.
However, relying on AI for risk management also introduces new AI-related risks that must be addressed through comprehensive AI risk management frameworks. Organizations must ensure AI tools used for risk management are themselves secure, unbiased, and operate within appropriate governance frameworks. This requires risk management practices that encompass both traditional risks and the unique risks associated with AI systems themselves.
Implementing Effective AI Risk Management Practices
Risk management practices require an understanding of the components of an AI system and the generic AI risks as well as the risks associated with AI relevant to particular use cases. Successful AI risk management depends on implementing comprehensive risk management processes that address all stages of AI development and AI deployment. DASF proposes seven steps to simplify this process:
- Have a mental model of an AI system and the components that need to work together during AI system development and deploying AI systems. Understanding the architecture of AI systems helps identify potential risks across different components.
- Understand the people and processes involved in building and managing AI systems and define their roles, including data scientists, engineers, and security teams. Clear role definition supports effective AI risk management by establishing accountability for risk management efforts.
- Understand what responsible AI entails and all the likely AI risks and catalog those AI-related risks across the AI components for effective AI risk management. This includes documenting potential risks related to AI security, data quality, bias, and ethical implications.
- Understand the various AI deployment models and risk implications for each throughout the AI lifecycle. Different deployment scenarios introduce different security risks and require tailored risk mitigation strategies.
- Understand the unique threats to your AI use cases and map your risks associated to those AI threats, considering potential risks from AI security threats, cyber threats, and security vulnerabilities.
- Understand the unique AI risks that apply to your AI use case and filter for those risks associated with AI based on your use cases and risk tolerance. Organizations must balance risk management requirements with business objectives.
- Identify and implement controls that need to be applied per your use case and deployment model, mapping each risk to AI components and controls through practical risk management approaches. This includes developing risk mitigation strategies specific to your AI applications.
With controls in place, AI-powered tools can help organizations detect and mitigate risks faster than traditional security measures. With adversarial training, machine learning algorithms can detect patterns and anomalies for active threat detection and provide continuous monitoring, automated incident response, behavioral analysis, and threat prediction as part of comprehensive risk management processes.
What is the 30% Rule in AI?
The 30% rule in AI risk management refers to the principle that organizations should dedicate approximately 30% of their AI risk management efforts to continuous monitoring and assessment of AI systems post-deployment. This ensures AI system's performance remains aligned with intended outcomes and helps identify potential risks that emerge during production use.
Effective AI risk management requires ongoing risk assessment rather than one-time evaluation during AI development. The 30% rule emphasizes that AI risk management practices must extend beyond initial AI system development and AI deployment phases. Organizations should allocate significant resources to conducting regular risk assessments, monitoring AI models for drift, detecting emerging risks, and updating risk mitigation strategies as AI technologies and threat landscapes evolve.
This continuous approach to AI risk management helps organizations detect security threats, system failures, and unintended consequences before they escalate into major incidents. By dedicating resources to ongoing risk management efforts, organizations can maintain data integrity, ensure AI security, and address risks proactively rather than reactively. The 30% rule supports responsible AI practices by ensuring AI systems receive consistent oversight throughout their operational lifecycle.
You can't have AI without high-quality data, and you can't have high-quality data without data governance and oversight. Effective governance and oversight ensure:
- Easy discoverability and seamless collaboration through the unification of data and AI assets, and the ability to catalog data collection sources from various systems.
- Secure data assets with a centralized approach to enforcing fine-grained access controls, auditing and governance policies to protect sensitive data and sensitive information.
- High-quality training data and fair, unbiased machine learning models with AI-powered monitoring that proactively identifies errors, conducts root cause analysis, and upholds the quality standards of both data and AI pipelines through data integrity controls.
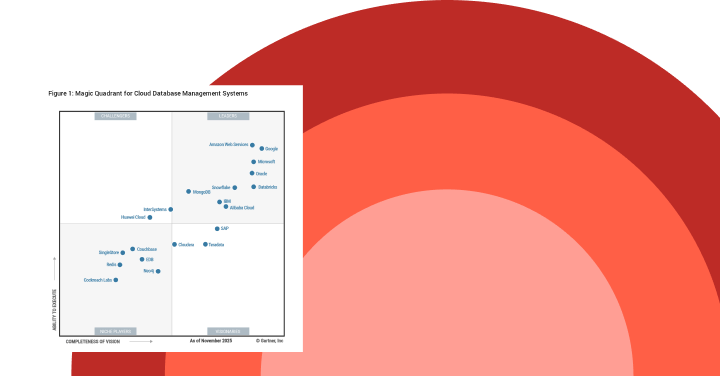
Gartner®: Databricks Cloud Database Leader
Addressing Generative AI Risks and Security Threats
Unlike traditional IT security, AI introduces new vulnerabilities that span data, models, infrastructure and governance. In the DASF, we identified 62 distinct AI risks across the 12 components of an AI system. At a high level, these potential risks include:
Data Operations risks, such as insufficient access controls, missing data classification, poor data quality, lack of data access logs and data poisoning that affect training data quality.
Model operations risks, such as experiments not being tracked and reproducible, model drift, stolen hyperparameters, malicious libraries and evaluation data poisoning affecting AI models.
Model deployment and serving risks, such as prompt injection, model inversion, denial of service (DOS), LLM hallucinations and black-box attacks during AI deployment.
Operations and platform risks, such as a lack of vulnerability management, penetration testing and bug bounty, unauthorized privileged access, a poor software development lifecycle (SDLC) and regulatory compliance issues.
The implications for these AI risks span a range of unwanted and costly consequences:
- Security and privacy breaches, as the data sent to an external LLM could be leaked or summarized, creating AI security threats
- Sensitive data and sensitive personal data being unintentionally sent by users to external AI systems
- Data loss, breach of data confidentiality, model theft and security risks
- Non-compliance with existing and evolving regulations like the EU AI Act and other regulatory compliance requirements
- Customer-facing AI systems that send data related to a different organization, creating unfair outcomes
Managing misinformation and bias also becomes crucial with generative AI and machine learning models. AI-powered monitoring can proactively identify errors, conduct root cause analysis, and uphold the quality standards of both data and AI pipelines. AI tools can also aid in risk prediction, combining AI and predictive analytics to provide real-time insights and actionable recommendations for business decision making, supporting effective AI risk management.
Resources and Tools for AI Risk Management Implementation
To strengthen AI risk management, teams should implement these measures with existing organizational policies and ensure proper oversight to build secure, resilient and aligned AI systems with business objectives while mitigating evolving threats in an increasingly AI-driven world. These risk management strategies are essential for responsible AI development and deploying AI systems securely:
- Authenticate and authorize access to your data to protect sensitive information, sensitive data, and input data from unauthorized access and security threats.
- Automate and quality check data before feeding it into model training to ensure data quality, prevent biased training data, and maintain data integrity throughout AI development.
- Govern, version and tag your data while tracking lineage to maintain data integrity, ensure data quality, and support regulatory compliance requirements.
- Enforce approval workflows to prevent AI models from being trained on unintended data sources, reducing risks associated with AI training processes and ensuring responsible AI development.
- Track model artifacts, datasets, versions and stakeholders for trust, explainability and responsibility in AI system development, supporting AI governance and risk management practices.
- Automate testing loss analysis after (re)training by evaluating model behavior on specific test inputs to identify potential risks, detect anomalies, and ensure AI system's performance meets expectations.
- Encrypt, authenticate and authorize AI models and endpoints while logging, auditing and monitoring access for AI security, protecting artificial intelligence systems from cyber threats and security vulnerabilities.
- Segregate LLMs and other AI models from internal and external systems to mitigate risks from security vulnerabilities, contain potential risks, and prevent system failures from cascading.
- Implement MLOps with HITL by enforcing permissions, versions, tags, ownership and approvals for production AI models in deploying AI systems, ensuring responsible AI practices throughout the AI lifecycle.
- Host AI models behind a gateway to rate limit safety filtering, personally identifiable information (PII) detection, topic moderation and keyword filtering, addressing AI security threats and protecting sensitive personal data.
- Audit and monitor data and AI models access at every stage of the AI lifecycle through continuous monitoring, conducting regular risk assessments, and implementing comprehensive risk management processes.
Implementing these practical risk management controls requires collaboration among data scientists, engineers, security teams, and governance personnel. Organizations should establish clear risk management frameworks that define responsibilities, escalation procedures, and response protocols for different types of AI risks. These frameworks should align with broader organizational risk tolerance and support both innovation and risk management objectives.
Secure data sharing and collaboration enables business leaders to gain accurate, timely and relevant insights for strategic decision-making. The Databricks Data Intelligence Platform provides a single point of access to securely consolidate and query data from multiple sources to quickly extract insights from structured and unstructured data through AI applications while maintaining AI security and data privacy.
By implementing strong AI governance, financial institutions cultivate a foundation of trust in their historical data, enabling AI systems to analyze large and complex AI models datasets swiftly and accurately. Trustworthy AI systems require comprehensive risk management efforts across the entire organization, from initial data collection through AI development, AI deployment, and ongoing operations.
Balancing Innovation and Risk in Artificial Intelligence
Responsible AI governance requires the organization to take accountability and control over their data and AI models with comprehensive continuous monitoring, privacy controls and AI governance throughout the AI development and AI deployment process. Accountability can no longer be assigned solely to the CIO to balance innovation and AI security while aligning with business priorities. There needs to be a common understanding among business, data, security teams, privacy and governance teams to unlock AI's full potential through responsible AI practices.
Artificial intelligence systems must be developed with responsible AI development principles that prioritize transparency, fairness, and accountability. Organizations implementing AI risk management practices should focus on conducting regular risk assessments, implementing risk mitigation strategies, and maintaining trustworthy AI systems that deliver business value while managing risks effectively.
Databricks is collaborating with NIST in the Artificial Intelligence Safety Institute Consortium to establish a new measurement science that will enable the identification of proven, scalable, and interoperable measurements and methodologies to promote the development of trustworthy AI systems and their responsible use. This collaboration supports the broader AI risk management frameworks and management framework AI RMF principles.
Emerging risks will impact the development and use of both standalone AI models and the agentic AI systems that Databricks is increasingly seeing its customers utilize to build AI applications with domain-specific Agents. Human error costs regulated businesses billions and those losses can be tracked to data problems and the volume of historical data that needs to be tracked. AI can assist risk management and regulatory compliance efforts by spotting anomalies, trends, and patterns that humans may not catch and generating alerts based on a set of rules.
Use the Databricks AI Security Framework for essential guidance for securely developing, deploying AI systems, and maintaining AI models at scale through comprehensive AI risk management frameworks. The framework assists organizations in ensuring their AI models remain secure and continue to deliver business value while addressing AI-related risks and implementing practical risk management across all AI technologies. This comprehensive approach to AI risk management helps organizations balance innovation with security threats mitigation and regulatory compliance.
Never miss a Databricks post
What's next?

Data Science and ML
June 12, 2024/8 min read
Mosaic AI: Build and Deploy Production-quality AI Agent Systems
AI
January 7, 2025/6 min read