What is Data Security?
Data security is a set of practices and technologies that protect digital data from unauthorized access, theft, corruption, poisoning or accidental loss while preserving its confidentiality, integrity and availability across the data lifecycle. Data security should help protect sensitive data (personally identifiable information, financial information, health information and intellectual property) throughout the data lifecycle, from creation to destruction. It should encompass everything from the physical security of hardware and storage devices to administrative and access controls, security of software applications, and data governance policies.
In today’s highly connected world, cybersecurity threats and insider risks are a constant concern. Organizations need to have visibility into the types of data they have, prevent the unauthorized use of data, and identify and mitigate risks around that data. The following sections will cover why data security is essential, common data security risks, and data security best practices to help protect your organization from unauthorized access, theft, corruption, poisoning or accidental loss.
Here’s more to explore
Why is data security important?
Data is one of the most critical assets for any organization today, so the importance of data security cannot be overstated. Data protection should be a priority for every business in every industry. This is increasingly important as data security breaches continue to grow. According to Check Point Research, global cyberattacks grew 38% in 2022 compared to 2021.
Business and regulatory impact
Protecting data is critical because data loss or misuse can have severe consequences for an organization.
- Reputational damage and loss of customer trust.
- Inaccurate ML models and degraded analytics from poisoned or corrupted data.
- Loss of business, revenue and long-term brand equity.
- Compromised intellectual property that weakens competitive advantage.
- Regulatory fines and legal penalties under frameworks such as GDPR and CCPA.
Data security risks
There are several types of data security risks. Some of the most common are:
Malware
Malware can include worms, viruses or spyware that enable unauthorized users to access an organization’s IT environment. Once inside, those users can potentially disrupt IT network and endpoint devices or steal credentials.
Ransomware
Ransomware infects an organization’s devices and encrypts data to prevent access until a ransom is paid. Sometimes, the data is lost even when the ransom demand is paid.
Phishing
Phishing is the act of tricking individuals or organizations into giving up information like credit card numbers or passwords or access to privileged accounts. The intent is to steal or damage sensitive data by pretending to be a reputable company with which the victim is familiar. External attackers may also pose as legitimate users to access, steal, poison or corrupt data.
Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks
A DDoS attack targets websites and servers by disrupting network services to overrun an application’s resources. The perpetrators behind these attacks flood a site with traffic to slow website functionality or cause a total outage.
Human error
Employees may accidentally expose data to unintended audiences as they access it or share it with coworkers. Or an employee may sign in to company resources over an unsecured wireless connection.
Insider threats
Disgruntled employees may intentionally expose data or seek to profit from data theft.
Data security tools and strategies
Data security tools and strategies enhance an organization’s visibility into where its critical data resides and how it is used. When properly implemented, robust data security strategies not only protect an organization’s information assets against cybercriminal activities but also promote data loss prevention by guarding against human error and insider threats, two of the leading causes of data breaches today.
Common data security tools
- Data encryption: Uses an algorithm to scramble normal text characters into an unreadable format. Encryption keys then allow only authorized users to read the data.
- Data masking: Masks sensitive data so that development can occur in compliant environments. By masking data, organizations can allow teams to develop applications or train people using real data.
- Data erasure: Uses software to overwrite data on any storage device completely. It then verifies that the data is unrecoverable.
- Access management: Includes policies, audits and technologies to ensure that only the right users can access technology resources.
- Role-based access management: Controls access to resources where permitted actions on resources are identified with roles rather than individual subject identities.
Data security best practices
Data security best practices include data protection tools such as those outlined in the previous section as well as auditing and monitoring. Data security best practices should be leveraged both on-premises and in the cloud to mitigate the threat of a data breach and to help achieve regulatory compliance. Specific recommendations can vary but typically call for a layered data security strategy architected to apply a defense-in-depth approach to mitigate different threat vectors.
Core data security best practices
- Use layered, defense-in-depth architectures that combine multiple controls to address different threat vectors.
- Apply security controls consistently across on-premises and cloud environments.
- Continuously audit and monitor access, configurations and data usage to detect anomalies quickly.
- Implement strong data governance policies that define how data is classified, accessed, used and retained.
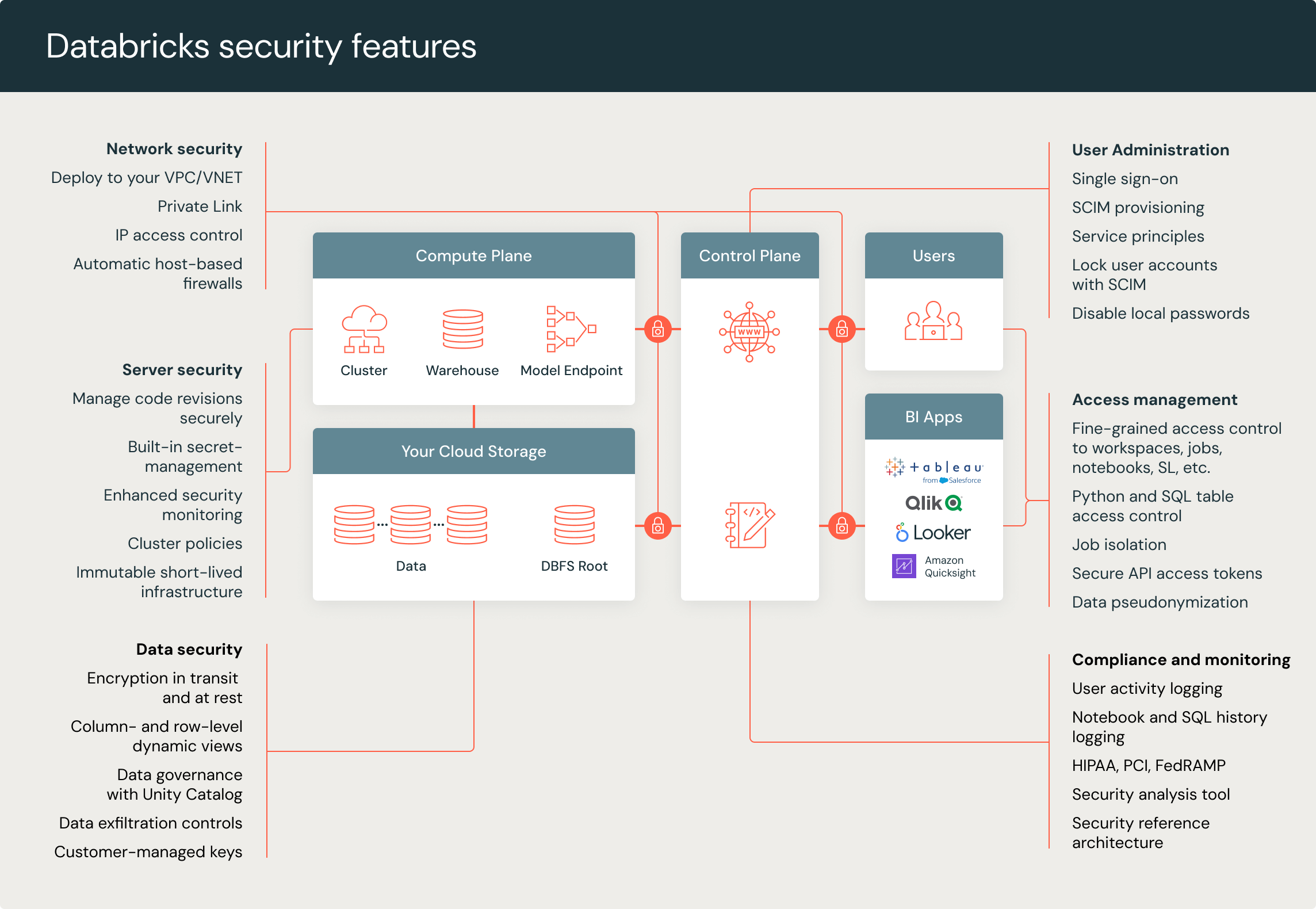
Securing data on the Databricks Data Intelligence Platform
The Databricks Data Intelligence Platform provides end-to-end security to ensure data is accessed properly, by authorized individuals, while helping organizations meet compliance requirements. Databricks provides comprehensive security to protect your data and workloads, including encryption, network controls, data governance, and auditing. We also offer best practices whitepapers, a security analysis tool, and terraform templates in the Databricks Security and Trust Center.
Databricks’ data governance solution, Unity Catalog, offers fine-grained data governance, centralized metadata and user management, centralized data access controls, data lineage, and data access auditing to seamlessly govern structured and unstructured data, machine learning models, notebooks, dashboards, and files on any cloud or platform.